Table of contents
The Aadhaar-enabled Payment System (AePS) is an initiative to enhance the ease of banking and financial services in India, especially for those in rural and remote areas. It leverages the Aadhaar biometric identification system to facilitate financial transactions and services.
Here's an overview of its functioning and significance:
How does AePS work?
- Aadhaar Linking: Individuals link their Aadhaar number (a unique 12-digit identification number) with their bank accounts.
- Biometric Authentication: During transactions, the customer's identity is authenticated using biometric data (like fingerprints or iris scans) linked to their Aadhaar number.
- Point of Transaction: Transactions can be carried out at various points like Micro ATMs or banking correspondents equipped with biometric devices.
- UIDAI and NPCI: The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) oversees Aadhaar, while the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) manages the backend of AePS, ensuring secure and smooth transactions.
Types of Transactions
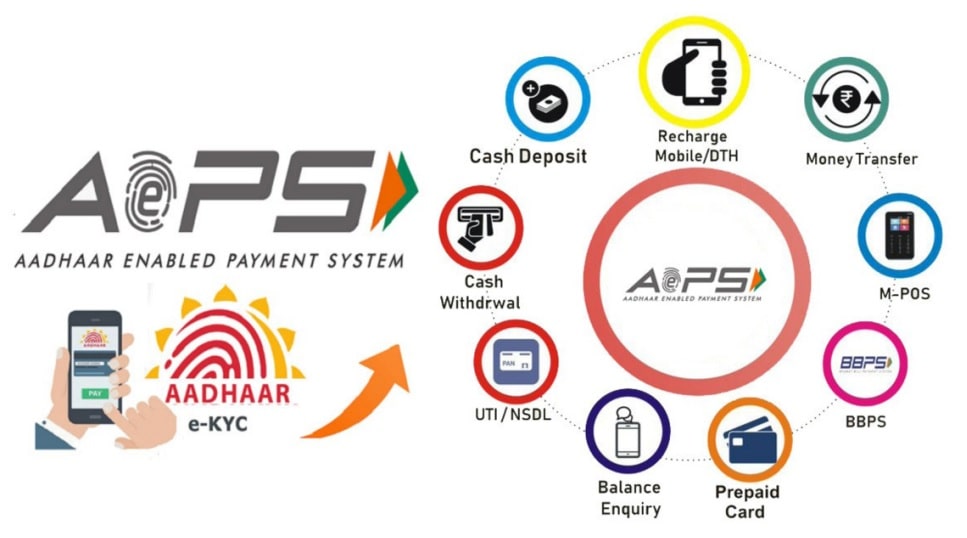
- Cash Withdrawal: Customers can withdraw money from their bank accounts using their Aadhaar number and biometric authentication.
- Cash Deposit: Depositing cash into a bank account through AePS is also possible.
- Balance Enquiry: Customers can check their account balance.
- Fund Transfer: AePS allows for the transfer of funds between Aadhaar-linked accounts.
Advantages
- Financial Inclusion: AePS plays a crucial role in promoting financial inclusion by making banking services accessible to the unbanked and underbanked populations.
- Reduced Dependence on Physical Banking: It minimizes the need for physical banking infrastructure, which is beneficial in remote or rural areas.
- Security and Transparency: Biometric authentication adds a layer of security and reduces the risk of fraud.
- Ease of Use: The system is user-friendly, especially for those who are not tech-savvy or do not have access to smart devices.
- Direct Benefit Transfer: AePS facilitates the direct transfer of government benefits and subsidies to the beneficiaries’ bank accounts, eliminating middlemen and reducing corruption.
Challenges
- Biometric Authentication Issues: Issues like poor quality of fingerprints in manual laborers can lead to authentication failures.
- Privacy Concerns: There are concerns regarding the safety and privacy of biometric and demographic data.
- Digital Literacy: The effectiveness of AePS is contingent on the users' digital literacy levels.
Future Prospects
- AePS is expected to evolve with advancements in technology and increased digital literacy, further enhancing its reach and efficiency.
AePS represents a significant step towards leveraging technology for financial empowerment and inclusive growth in India. As it evolves, addressing its challenges will be crucial to maximize its potential benefits.
Previous Post