Table of contents
Relevance for UPSC
- Geopolitics: Implications for India's West Asia policy and energy security.
- Ethics: Humanitarian concerns, rights of refugees, and conflict resolution.
- IR Syllabus: Bilateral relations, India's position on global conflicts, and UN peacekeeping.
Introduction
The Israel-Palestine conflict is one of the most enduring and contentious disputes in modern history. Rooted in historical, religious, and political contexts, it remains a focal point in international relations. Understanding the geopolitical dynamics, historical background, and the socio-economic implications of the conflict is crucial for UPSC aspirants.
Map of Israel and Palestine
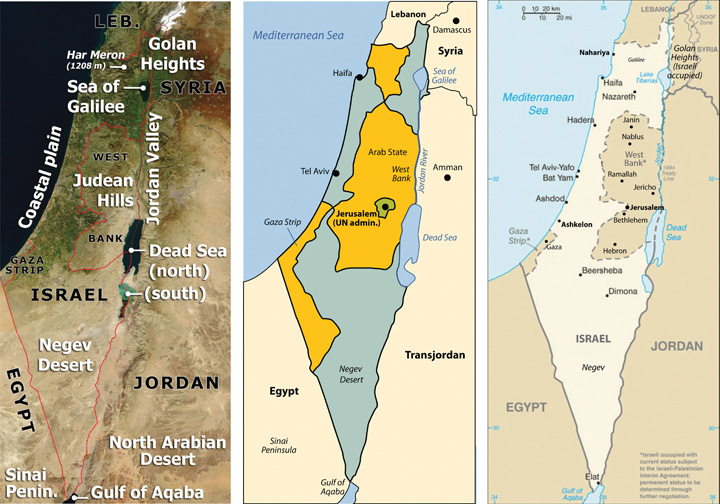
Major Locations in Israel-Palestine Region
1. Locations Frequently in News
Jerusalem
- Significance: Central to the Israel-Palestine conflict; claimed as the capital by both nations.
- Geographical Features: Located on a plateau in the Judean Mountains, between the Mediterranean Sea and the Dead Sea.
Gaza Strip
- Significance: A densely populated Palestinian territory under Hamas control; frequently involved in armed conflicts with Israel.
- Geographical Features: Narrow coastal plain along the Mediterranean Sea, bordering Egypt and Israel.
West Bank
- Significance: Palestinian territory with Israeli settlements and contested boundaries; includes key cities like Ramallah, Hebron, and Bethlehem.
- Geographical Features: Hilly terrain west of the Jordan River.
Tel Aviv
- Significance: Economic and technological hub of Israel; frequent location for diplomatic and tech-related summits.
- Geographical Features: Situated on Israel’s Mediterranean coastline.
Hebron
- Significance: Religious site housing the Tomb of the Patriarchs; a flashpoint for Israeli-Palestinian tensions.
- Geographical Features: Rugged terrain in the southern West Bank.
Nablus
- Significance: Economic hub of the West Bank and a key center of Palestinian resistance.
- Geographical Features: Nestled between Mount Ebal and Mount Gerizim.
Ramallah
- Significance: Administrative center of the Palestinian Authority.
- Geographical Features: Elevated city in the central West Bank, at 880 meters above sea level.
Ashkelon
- Significance: Frequently in the news due to its proximity to Gaza and vulnerability to cross-border attacks.
- Geographical Features: Coastal city along the Mediterranean.
2. Geographical Features
Rivers
- Jordan River: Key water source; forms the boundary between Israel, the West Bank, and Jordan. Vital for agriculture and a significant geographical boundary.
Seas
- Mediterranean Sea: Western border of Israel and the Gaza Strip; important for trade and defense.
- Dead Sea: Shared by Israel, the West Bank, and Jordan; lowest point on Earth, renowned for its high salinity.
Deserts
- Negev Desert: Covers southern Israel, including Beersheba; known for arid climate and strategic importance.
Mountains and Plateaus
- Judean Mountains: Range running through Jerusalem and the West Bank; significant for its historical and religious sites.
- Mount Carmel: Near Haifa, important for its cultural and ecological significance.
- Golan Heights: A disputed plateau providing strategic military advantage; known for its freshwater sources.
3. Other Important Locations in News
Bethlehem
- Significance: Christian pilgrimage site; believed to be the birthplace of Jesus.
- Geographical Features: Located in the Judean Hills, West Bank.
Haifa
- Significance: Major port city and industrial hub.
- Geographical Features: Situated on the northern slopes of Mount Carmel along the Mediterranean.
Eilat
- Significance: Key port and tourist destination for Israel on the Red Sea.
- Geographical Features: Southernmost city of Israel, bordering the Red Sea.
Beersheba
- Significance: Gateway to the Negev Desert; known for its historical significance.
- Geographical Features: Located in the northern Negev Desert.
Jaffa
- Significance: Historic port city now part of Tel Aviv; significant for cultural heritage.
- Geographical Features: Coastal city along the Mediterranean.
Jericho
- Significance: Among the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world.
- Geographical Features: Situated near the Jordan River in the West Bank, below sea level in an oasis.

Israel: Country Profile
Geography
- Location: Middle East, bordered by Lebanon (north), Syria (northeast), Jordan (east), Egypt (southwest), and the Mediterranean Sea (west).
- Area: Approximately 22,072 sq km (including East Jerusalem and the Golan Heights).
- Climate: Mediterranean in the coastal regions, arid in the southern Negev desert.
Demographics
- Population: ~9.7 million (2024 estimate).
- Ethnic Composition: Predominantly Jewish (~74%), with Arab minorities (~21%) and others (~5%).
- Languages: Hebrew (official), Arabic.
- Religion: Judaism (primary), Islam, Christianity, Druze.
Political System
- Type: Parliamentary democracy.
- Capital: Jerusalem (contested internationally; Tel Aviv recognized by most nations).
- Key Figures: Prime Minister (Head of Government), President (Ceremonial Head of State).
Economy
- GDP: $500 billion (2024 estimate).
- Major Industries: High-tech, defense, pharmaceuticals, agriculture.
- Strategic Importance: Advanced technology hub; critical ally of the U.S. in the Middle East.
Foreign Relations
- Allies: United States, European Union.
- Challenges: Tensions with neighboring Arab states, Iran's nuclear program, and the Palestine issue.
Conflict Overview
- Israel controls areas contested by Palestinians, including the West Bank, Gaza Strip (blockaded), and East Jerusalem.
- Key disputes: Territorial boundaries, status of Jerusalem, right of return for Palestinian refugees.
Palestine: Country Profile
Geography
- Territories: West Bank, Gaza Strip, and East Jerusalem.
- Borders: Israel surrounds the West Bank; Gaza shares a border with Egypt and Israel.
- Area: ~6,220 sq km.
- Climate: Mediterranean in the west, arid in the east.
Demographics
- Population: ~5.2 million (2024 estimate).
- Ethnic Composition: Predominantly Arab.
- Languages: Arabic (official), Hebrew (spoken by some).
- Religion: Islam (~98%), Christianity (~1%), others.
Political System
- Governance: Divided between two political factions:
- Fatah: Controls the West Bank (recognized internationally as the Palestinian Authority).
- Hamas: Governs the Gaza Strip (considered a terrorist organization by several countries).
- Capital: Claims East Jerusalem; de facto governance split between Ramallah (Fatah) and Gaza City (Hamas).
Economy
- GDP: ~$15 billion (2024 estimate).
- Challenges: High unemployment, dependency on foreign aid, restrictions imposed by Israel.
- Key Industries: Agriculture, small-scale manufacturing.
Foreign Relations
- Allies: Support from Arab League nations, Turkey, Iran, and some non-aligned countries.
- International Status: Recognized as a non-member observer state by the United Nations.
Conflict Overview
- Key Issues: Territorial sovereignty, Israeli settlements in the West Bank, access to resources, blockade of Gaza, and the refugee crisis.
- Notable Agreements: Oslo Accords (1993-95), which established limited Palestinian self-rule in parts of the West Bank and Gaza.
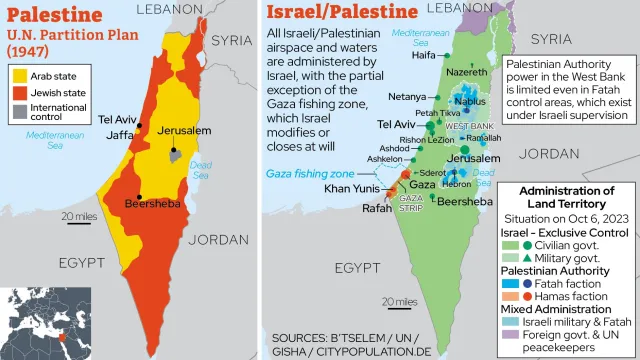
Historical Context
Pre-1948
- Ottoman Empire ruled the region until World War I.
- British Mandate (1920–1948): Period of increasing Jewish immigration amidst Arab resistance.
- 1947: UN Partition Plan proposed separate Jewish and Arab states, rejected by Arabs.
Post-1948
- 1948: Establishment of Israel; neighbouring Arab states attacked but were defeated.
- Result: Massive displacement of Palestinians (Nakba) and the establishment of Israeli control over large areas.
Post-1967
- Six-Day War: Israel captured the West Bank, Gaza Strip, East Jerusalem, Golan Heights, and Sinai Peninsula (later returned to Egypt).
- Continued settlement activity in occupied territories and military control over Gaza and the West Bank.
Contemporary Issues
- Hamas vs. Israel conflicts: Frequent escalations, including the 2021 and 2023 wars.
- International interventions: U.S., UN, and Qatar and other regional players attempt mediation, but no permanent resolution has been achieved.
Key International Stakeholders
United States
- Strong ally of Israel; broker of several peace efforts.
- Military and economic aid to Israel.
United Nations
- Recognizes Palestine as a non-member observer state.
- Calls for a two-state solution.
Arab States
- Initially adversarial towards Israel; now divided:
- Egypt and Jordan signed peace treaties with Israel.
- UAE, Bahrain, and Morocco normalized relations under the Abraham Accords (2020).
India's Position
- Historical Support: Backed Palestine's statehood post-independence.
- Current Strategy: Balances relations with Israel (defence, tech) and Palestine (development aid, moral support).
- Recent Actions: India has advocated for a two-state solution and expressed concerns over violence in Gaza.
Key Terms for UPSC
- Two-State Solution: Proposal for Israel and Palestine to exist as separate, sovereign nations.
- Oslo Accords: Framework agreements aiming for peace and Palestinian self-governance.
- Nakba (Catastrophe): Term used by Palestinians to describe their displacement in 1948.
- Abraham Accords: Agreements normalizing ties between Israel and several Arab nations.
- UNRWA (United Nations Relief and Works Agency): Provides aid to Palestinian refugees.

Write UnLimited Course (1 Year)
Write answers from any source, we will evaluate them for you.
