Table of contents
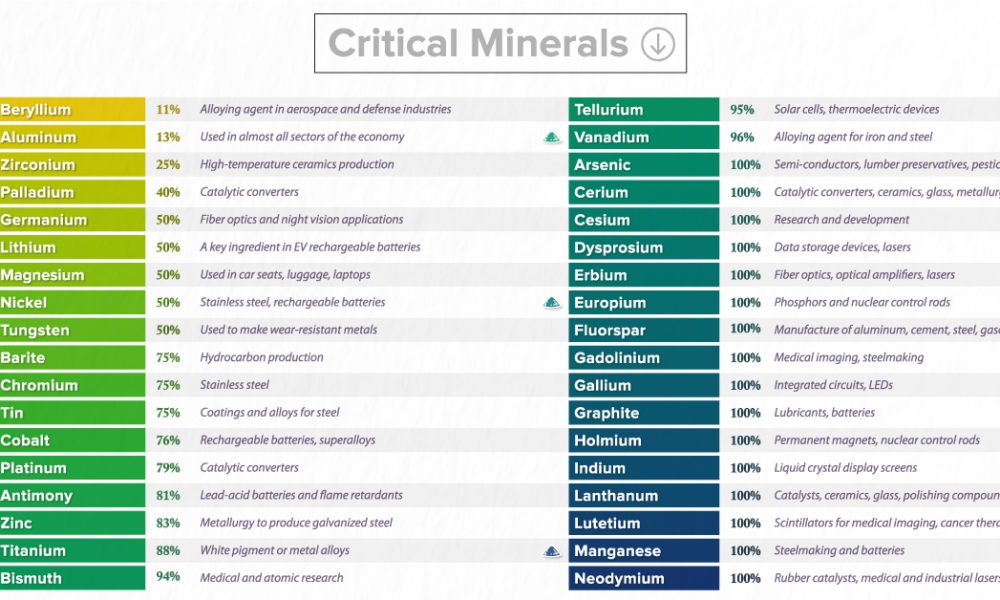
Critical minerals are essential raw materials that are crucial for the economic and national security of a country. The term "critical" refers to the importance of these minerals in the supply chain and the potential risk of supply disruptions.
Definition
- Definition: Critical minerals are essential for the functioning of modern technologies and industries but are at risk of supply chain disruptions.

Importance
- They are used in a wide range of applications, including electronics, renewable energy, aerospace, defence, and telecommunications.
- These minerals are vital for the production of high-tech devices, renewable energy technologies, and various industrial applications.
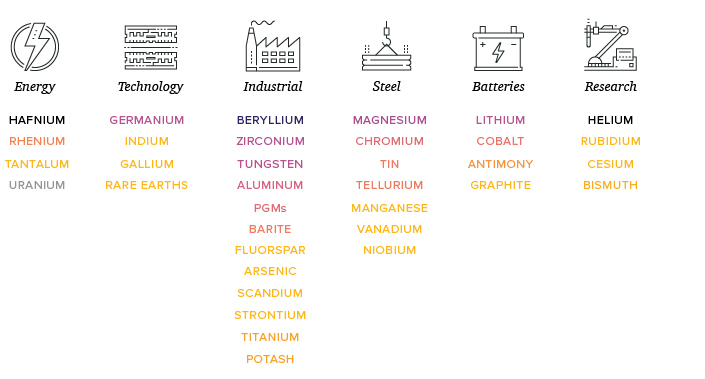
Applications
- Graphite: Used in batteries, especially for electric vehicles (EVs) and energy storage systems.
- Gallium: Used in semiconductors, LEDs, and solar panels.
- Germanium: Used in fiber optics, infrared optics, and solar cells.
- Lithium: Essential for rechargeable batteries in EVs, laptops, and smartphones.
- Cobalt: Used in batteries, superalloys, and catalysts.
- Rare Earth Elements (REEs): Used in magnets, electronics, and various high-tech applications.
Minerals and their Sources
- Lithium:
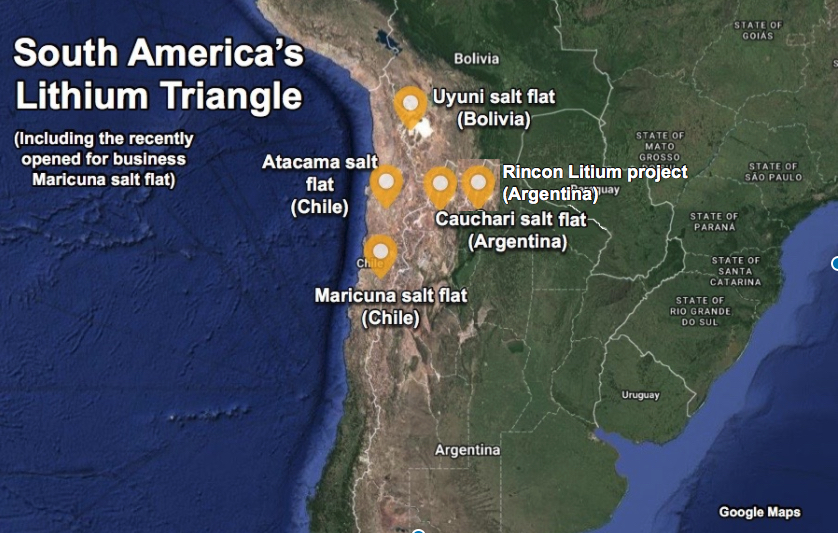
- Australia: One of the largest producers of lithium.
- Argentina and Chile: Part of the "Lithium Triangle," which holds a significant portion of the world's lithium reserves.
- Cobalt:
- Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC): The largest producer of cobalt, though India is looking to diversify its sources due to geopolitical and ethical concerns.
- Rare Earth Elements (REEs):
- China: Currently the dominant supplier of rare earth elements globally. However, India is seeking to reduce its dependence on China by exploring other sources.
- Africa: Potential new sources of rare earth elements.
- Graphite:
- China: The largest producer of natural graphite.
- Mozambique and Madagascar: Emerging sources of graphite.
- Gallium and Germanium:
- China: Major producer of both gallium and germanium.
- Other Potential Sources: India is exploring opportunities to secure these minerals from other countries to diversify its supply chain.

India's Strategic Initiatives
India sources its critical minerals from both domestic and international sources. Given the strategic importance of these minerals for various high-tech and industrial applications, India has been actively working to secure a stable and diversified supply chain.

- In July 2023, India released a list of 30 critical minerals essential for the country's economic and technological development.
- India has established a joint venture company, Khanij Bidesh India Ltd. (KABIL), with contributions from National Aluminium Company Ltd, Hindustan Copper Ltd, and Mineral Exploration and Consultancy Ltd.
- KABIL is exploring opportunities to acquire critical mineral assets in countries like Australia, Argentina, and Chile.
Domestic Sources
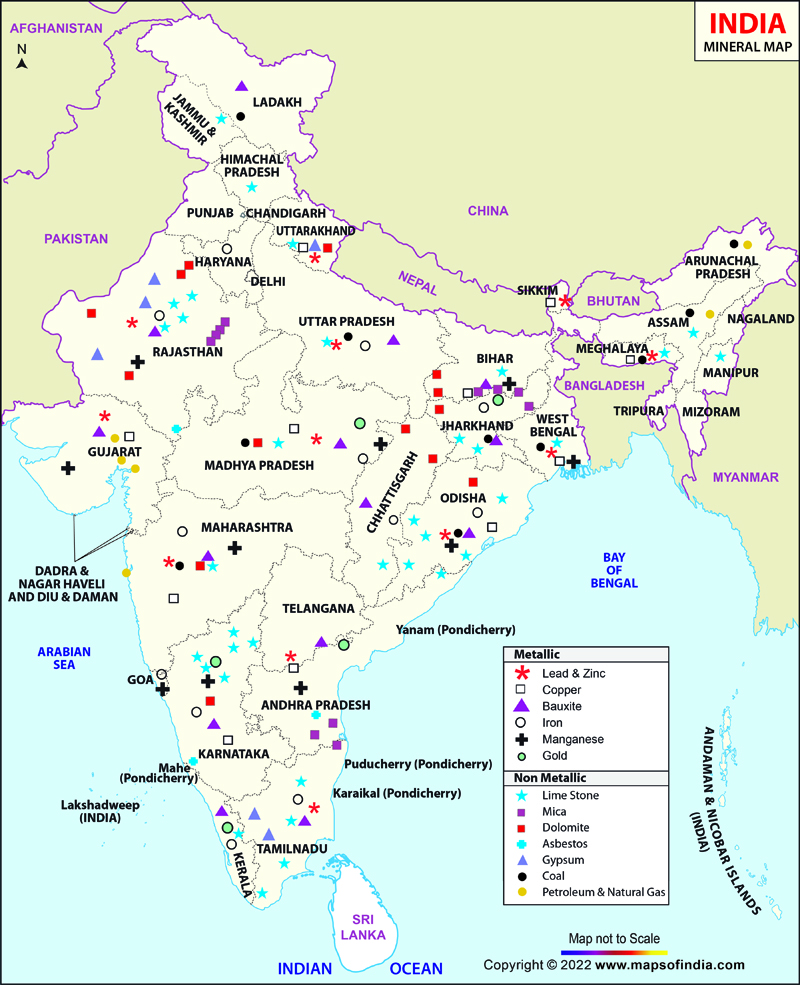
- Exploration and Mining within India:
- The Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957, was updated through the MMDR Amendment Act, 2023, to enhance the exploration and mining of critical minerals within India.
- Exploration and Mining: Efforts have been expanded to identify and develop domestic sources, ensuring sustainable and responsible mining practices.
International Sources


Joint Ventures and Acquisitions Abroad
- Khanij Bidesh India Ltd. (KABIL): India has established a joint venture company, KABIL, with equity contributions from -
- National Aluminium Company Ltd.
- Hindustan Copper Ltd.
- Mineral Exploration and Consultancy Ltd.
- KABIL's objective is to acquire critical mineral assets abroad to ensure a consistent supply to the Indian domestic market.
Bilateral Agreements and Partnerships
- India-U.S. Cooperation:
- India and the U.S. are working towards a bilateral agreement to enhance cooperation on critical minerals.
- This includes promoting India’s role in the mineral security partnership and co-investing in lithium resource projects in South America and rare earth deposits in Africa.
- Supply Chain Partnerships: The partnership aims to strengthen supply chains for critical minerals like graphite, gallium, and germanium.
- India-Australia, India-Argentina, and India-Chile Partnerships: Focus on lithium and other minerals through KABIL ventures and strategic agreements.
- India-Africa Partnerships: Diversifying sources of rare earth elements and other minerals.
- India-Canada and India-Russia Partnerships: Collaboration on a variety of critical minerals, including cobalt, nickel, and rare earth elements.
Read about: Bilateral Partnerships for Critical Mineral
Implications
- Economic and National Security:
- Ensuring a stable supply of critical minerals is essential for countries' economic growth and national security.
- Disruptions in the supply chain of critical minerals can have significant impacts on various industries and technological advancements.
- Technological Advancements:
- Critical minerals are fundamental to developing and deploying cutting-edge technologies, including renewable energy systems, electric vehicles, and advanced electronics.
- Securing access to these minerals is crucial for maintaining technological leadership and innovation.
- Sustainable Development:
- The extraction and processing of critical minerals must be done responsibly and sustainably to minimize environmental impacts and ensure long-term availability.
- International cooperation and investment in sustainable mining practices are essential to achieve this goal.
Conclusion
Critical minerals play a vital role in modern economies and technological advancements. The establishment of KABIL and the ongoing cooperation with countries like the U.S. are key components of this strategy.
For UPSC preparation, it is important to understand the geopolitical, economic, and environmental dimensions of critical mineral supply chains, as well as the policies and initiatives taken by India to secure these essential resources.
Previous Post