Subject: GS 1
Syllabus: Geography: Salient features of world’s physical geography.
Questions
- Local winds influence the weather of a small area but are still important due to their impact on human lives. Enumerating the local winds globally. Highlight their impacts. (150 Words, 10 Marks)
- Volcanism is an endogenic force. Briefly explaining the types of extrusive volcanism, mention the endogenic features developed on the Earth’s surface due to it. (150 Words, 10 Marks)
Model Structure
1. Local winds influence the weather of a small area but are still important due to their impact on human lives. Enumerating the local winds globally. Highlight their impacts. (150 Words, 10 Marks)
Model Structure
Introduction
- On a geographical scale, surface winds also include local winds that are gradient winds regulated by the local pressure profile. These local winds may be hot or cold depending on the prevailing climate.
Main body
- They include winds that are found all over the world in coastal and mountainous regions. Coastal winds include land and sea breezes and mountainous winds include anabatic and katabatic winds.
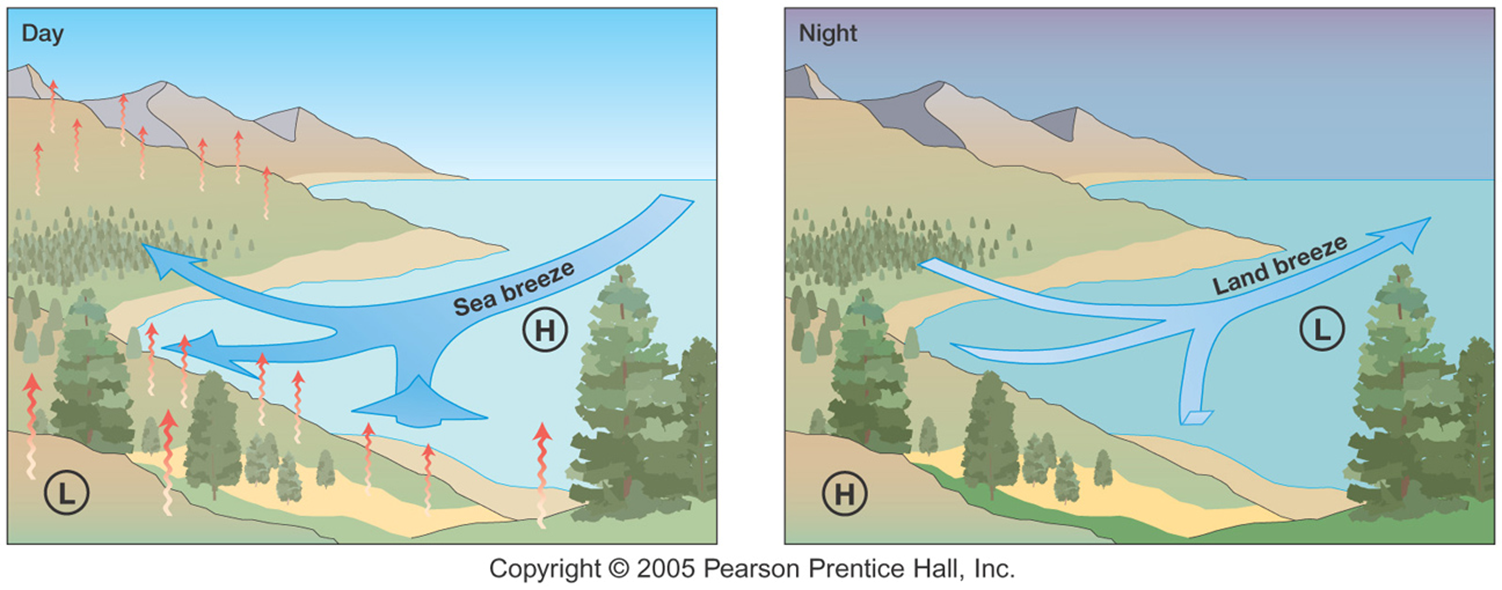
- Land and sea breezes are daily regulators of coastal weather due to the differential heating and cooling of land and water. But they are absent in equatorial and regions above 60 degrees latitude due to the negligible climatological difference between land and sea.
- Anabatic and katabatic winds owe their genesis to differential heating and cooling of the mountain wall and the valley floor. These parts also develop temperature inversion and regulate the demographic and economic significance of mountains.
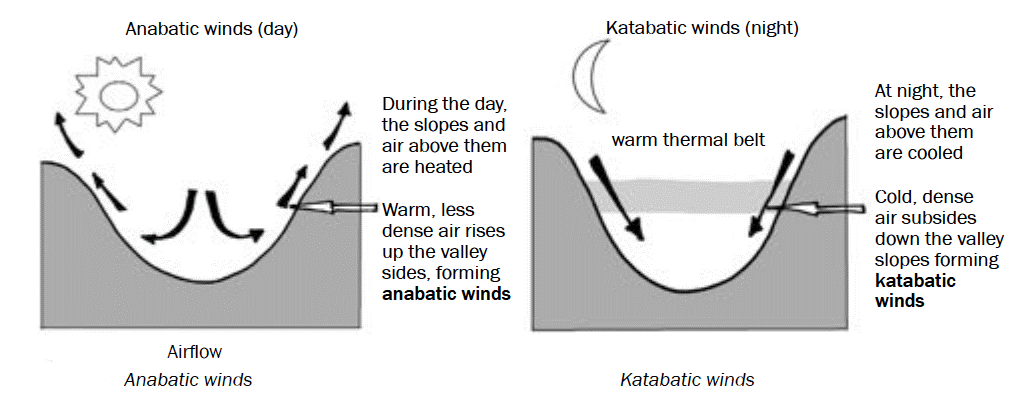
- Region-specific category of local winds includes winds like-
- Cold and dry winds - They represent polar outbreaks, thus confined to the low sun season. Some examples are Blizzards of North America, Purgas of Siberia and Pampero of Argentina.
- Hot winds - They regulate the weather of tropical desert areas and are typical of the high sun season. They are also called dust devils due to sudden heating of the land, which develops low pressure and hence sand particles are tossed up in the air. Winds include the Loo in Western India, Harmattan in upper Guinea, which reduces humidity levels, Sirocco, which blows over the Mediterranean sea and causes precipitation in nearby islands, and Khansein, which increases local temperature and causes heat strokes.
- Descending winds - All these are warm and dry, but can be favourable like Chinook in Canada and Foehn in Switzerland, which aid in melting mountain snow and increase local temperature. They can also be unfavourable, like Santa Ana in California and Shamoon in Iran, causing forest fires.
Conclusion
- As stated above, local winds are very important in the regulation of local weather conditions if they are favourable, but can be a health and environmental hazard if they are unfavourable.
2. Volcanism is an endogenic force. Briefly explaining the types of extrusive volcanism, mention the endogenic features developed on the Earth’s surface due to it. (150 Words, 10 Marks)
Model Structure
Introduction
- Volcanism is a sudden endogenic force that is capable of forming many relief features by the movement of molten magma from Earth’s interior to the surface.
- It results in the ejection of many materials based on composition, like magma, which can be felsic or mafic, gases and pyroclasts.
Main Body
- It is the location of ejected magma that makes it extrusive. The central type of ejection results in magma reaching Earth’s surface due to the presence of a well-defined pipe. These eruptions are located along active plate boundaries and based on intensity, there are four types of extrusive volcanism-
- Hawaiian- Oceanic intra-plate divergence, as seen in the Hawaiian Islands, where the complete absence of trapping of gases and less distance travelled by magma makes it quietest of all types.
- Strombolian- This involves comparatively stronger ejection due to trapped gases, but is still weaker than the next two types. It involves continental divergence areas as in Mount Kilimanjaro, and transverse boundaries, such as Mount Whitney.
- Vesuvian- It is very intense due to the absence of a clear passage for magma and is located along a convergent destructive boundary. It is associated with condensation and precipitation along with lahar i.e mass movement of water-saturated pyroclast.
- Pelean- It is the strongest of all and involves all of the Vesuvian activities, along with the blowing up of existing cones. The eruption is so strong that pyroclast reaches to heights of clouds and generate glowing clouds. Eg- Krakatoa and Martinique.
- These activities develop many endogenic features, which include a crater and caldera lake, a volcanic cone which may be a cinder or parasitic cone, and a plug dome.

UPSC Essential + Mentorship (New Batch)
One course for all your needs - Comprehensive Lectures, Test Series, 1:1 Mentorship, Notes, Current Affairs etc.
