Table of contents
Context
Recently, NITI Aayog’s Frontier Tech Hub launched the roadmap “Reimagining Manufacturing: India’s Roadmap to Global Leadership in Advanced Manufacturing”, which envisions India becoming a top-three global manufacturing hub by 2035. It lays down a 10-year strategic roadmap for integrating frontier technologies—AI, robotics, advanced materials, and digital twins—across 13 key manufacturing sectors to achieve Viksit Bharat @2047.
Current Status of India’s Manufacturing Sector
- Major industries: Automotive, Engineering, Chemicals, Pharmaceuticals, Electronics, Textiles, Consumer Durables.
- Supported by Make in India, PLI Schemes, and PM GatiShakti.
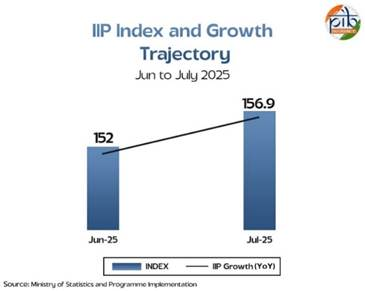
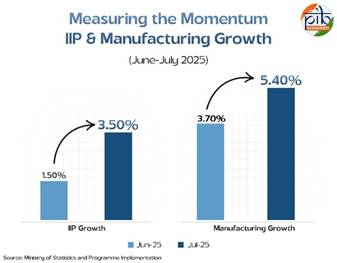
Significance of the Manufacturing Sector
1. Driver of Economic Growth
- Manufacturing anchors India’s growth engine with 16–17% GDP share and is projected to reach 25% by 2035.
- Sectors like automobiles, engineering, and electronics form the core of India’s industrial ecosystem.
2. Employment & Inclusive Development
- Employment in manufacturing rose from 6% (2004–14) to 15% (2014–24) (PIB, 2025).
- PM MITRA Parks aim for 20 lakh jobs; Footwear & Leather Mission targets 22 lakh jobs.
- Manufacturing fosters urban–rural, male–female inclusion through skill-based employment.
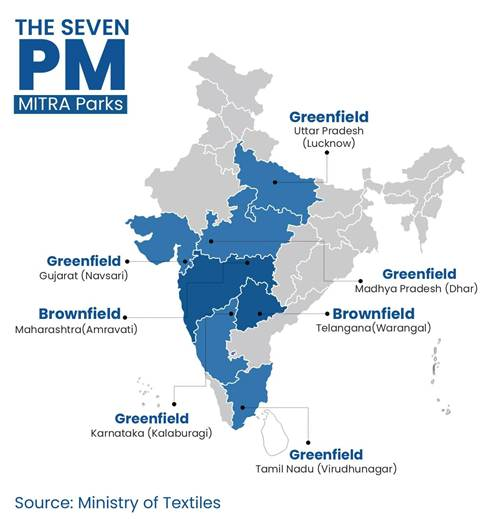
3. Export Competitiveness
- Exports (Q1 FY26): US$210.3 bn (+6% YoY) driven by engineering, chemicals, electronics.
- Electronics exports: US$29.1 bn (FY24) → US$38.6 bn (FY25) → est. US$50 bn (FY26).
- India supplies 50% of global vaccines, earning the tag Pharmacy of the World.
4. Investment & Industrial Ecosystems
- FDI inflows (2014–25): US$748.8 bn, with manufacturing FDI up 69% in a decade.
- PLI disbursed ₹21,534 crore, catalysing ₹1.76 lakh crore investment.
5. Technology-Driven Competitiveness
- Industry 4.0 tools (AI, digital twins, robotics) are enhancing productivity and quality.
- The HSBC PMI of 59.1 reflects high business confidence and export order growth.
6. Linkages & Multiplier Effects
- Strong interlinkages with logistics, energy, and services create multiplier effects.
- GatiShakti & National Logistics Policy enhance supply-chain efficiency.
7. Sustainable Industrialisation
- Initiatives like National Manufacturing Mission and Net Zero 2070 align with clean-tech goals—solar PV, EV batteries, wind turbines.


Opportunities and Potential
1. Pathway to a $1 Trillion Manufacturing Economy
- India aims for US$1 trillion manufacturing output by FY26.
- Manufacturing could contribute US$500 bn annually to the global economy by 2030.
2. Global Value Chain Integration
- Mobile exports: ₹1,500 crore (2014–15) → ₹2 lakh crore (2024–25).
- India is emerging as a China+1 alternative, with value addition in electronics up to 70%.
3. Industry 4.0 Transformation
- Adoption of AI, robotics, and advanced materials could add US$1 trillion to GDP by 2047.
- Initiatives: SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0, Digital Manufacturing Hubs.
4. Green Manufacturing
- ₹20,000 crore allocated in Budget 2025–26 for renewable manufacturing.
- India targets 10% of global wind component demand by 2030.
5. Expanding Domestic Demand
- By 2030, India’s middle class will form 17% of global consumption.
- E-commerce exports: US$1 bn → US$400 bn annually by 2030.
6. Investment Confidence
- FY25 FDI inflow: US$81 bn, of which US$19 bn in manufacturing.
- Global giants—Google (Pixel Tamil Nadu), Micron (₹23,771 crore Gujarat plant)—boost investor trust.
7. MSME and Startup Synergy
- MSMEs → 30% of manufacturing output.
- 1.91 lakh startups, generating 17.7 lakh jobs (DPIIT, 2025).
- MSME–startup collaboration fuels innovation and decentralisation.
8. Infrastructure & Industrial Corridors
- FY25: ₹28,602 crore in new corridor projects.
- Logistics cost to be cut below 8% of GDP by 2030 (World Bank LPI top 25 target).
9. Sunrise Sectors
10. Strategic Window (2025–2047)
- Timely adoption of frontier tech could make India the top 3 globally by 2035.
- Delay could cost US$270 bn by 2035 and US$1 tn by 2047 (NITI Aayog).
Challenges
Government Initiatives
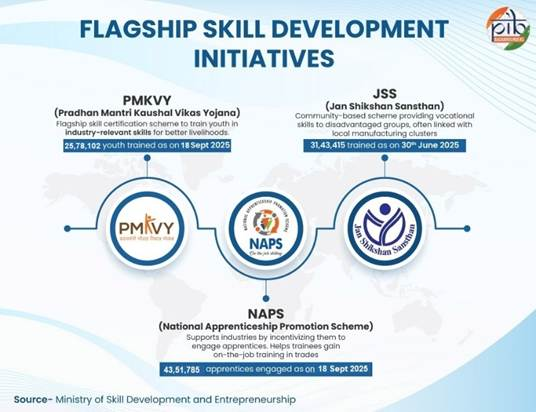
Way Forward
- Accelerate Technology Adoption – Integrate AI, robotics, and digital twins in cluster-based models.
- Empower MSMEs – Simplify credit, promote digital manufacturing & R&D linkages.
- Enhance Infrastructure – Fully operationalise GatiShakti and reduce logistics cost to <8% of GDP.
- Green Transition – Expand clean-tech production aligned with Net Zero 2070.
- Skilling & Innovation – Strengthen industry–academia partnerships; promote innovation hubs.
- Stable Policy Regime – Predictable regulatory environment for domestic and global investors.
Conclusion
India stands at a historic inflexion point in its industrial journey. By combining frontier technology adoption, green industrialisation, and inclusive workforce development, India can transition from a factor-driven to a technology-driven economy. If executed with consistency, the manufacturing sector can anchor the vision of a US$1 trillion manufacturing economy and realise the dream of a Viksit Bharat @2047.
Source: PIB
Download PDF
Courses by UPSCprep.com
A comprehensive range of courses meticulously designed to help you cover the syllabus in phases, without overwhelming you with long classes, ensuring you have ample time for self-study.
