Table of contents
SCO stands for the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation, which is a permanent intergovernmental Eurasian political, economic, and security alliance founded in 2001. It was established to promote cooperation and mutual support among its member states in areas such as trade, security, regional stability, and development.

Background and Evolution
- Origins:
- Evolved from Shanghai Five (China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, 1996–2001), focusing on border peace.
- SCO formed in June 2001, with Uzbekistan joining.
- Founding Date & Legal Status:
- Established on 15 June 2001 (Shanghai).
- SCO Charter signed 2002 (St. Petersburg), effective 19 Sep 2003.
- Legal status: Permanent international organisation.
- Headquarters & Languages:
- SCO Secretariat in Beijing (China), RATS headquarters in Tashkent (Uzbekistan).
- Official languages: Chinese, Russian.
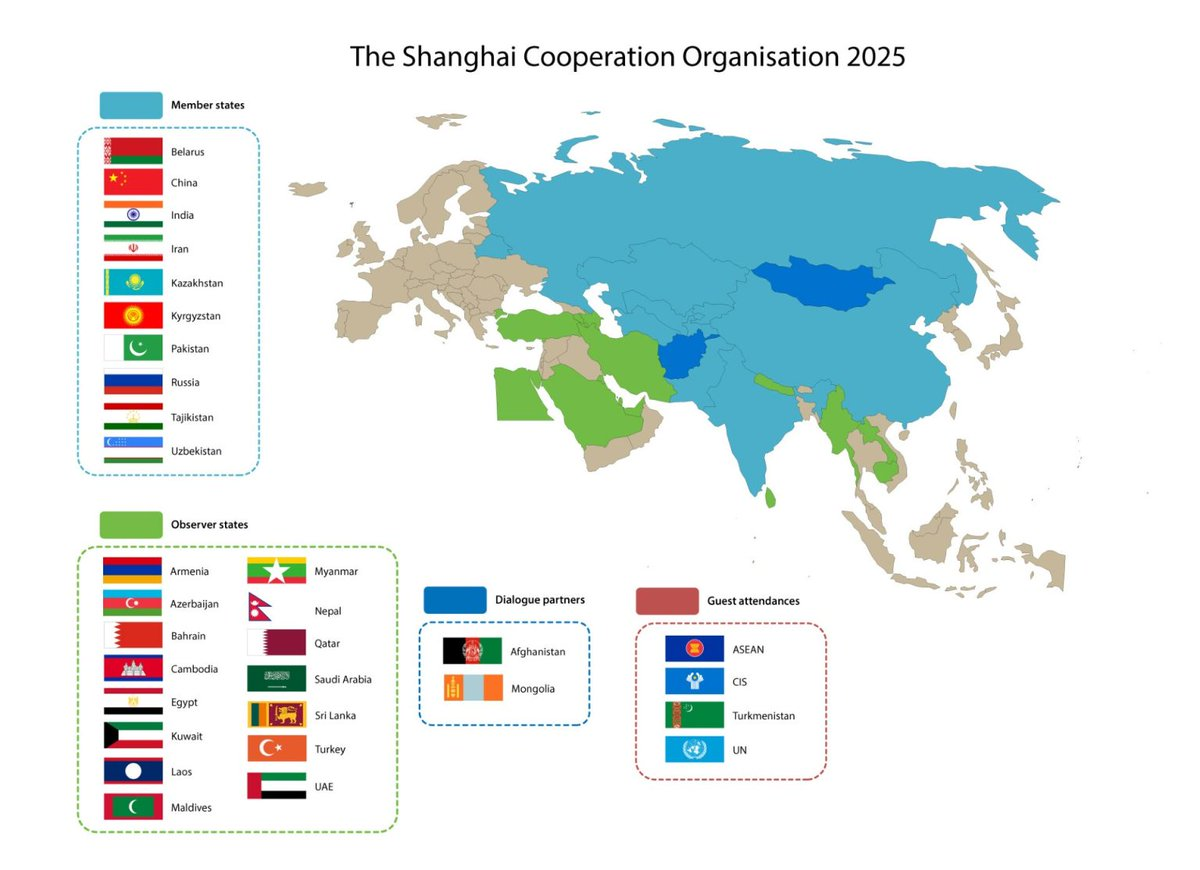
- Membership Expansion: From 6 states, expanded to 10 (India, Pakistan joined in 2017; Iran 2023; Belarus 2024).
- Observers & Dialogue Partners:
- Observer states: Afghanistan, Mongolia.
- Dialogue partners: Turkey, Sri Lanka, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, etc.
- Account for 43% global population and 23% global economy.

Objectives, Principles, & “Shanghai Spirit”
- Stated Objectives:
- Strengthen relations, promote cooperation (political, economic, scientific, cultural), maintain peace and stability, and pursue equitable order.
- Focus on fighting terrorism, separatism, and extremism (“Three Evils”).
- Shanghai Spirit:
- Core values—mutual trust, mutual benefit, equality, consultation, respect for diversity, pursuit of common development. Summit declarations often reiterate these.
- Security Focus:
- Joint military exercises (“Peace Mission”), RATS coordinates anti-terrorism.
- Strong emphasis on collective security against terrorism and extremism.
- Economic & Cultural Cooperation:
- SCO Business Council, Interbank Consortium.
- Initiatives in energy, transport, digital economy, cultural exchanges, youth programs, traditional medicine, science and technology.
- Indivisible Security & Multipolarity: Emphasis on equal security for all; opposes unilateralism, advocates a multipolar order.
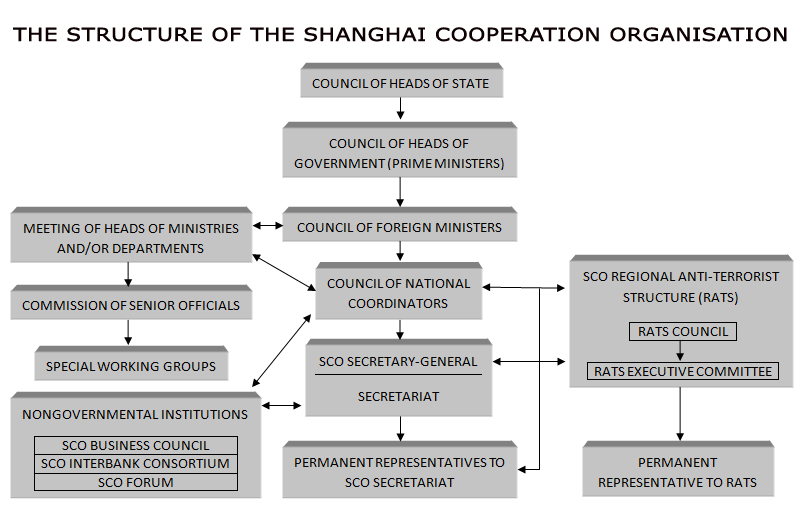
Organizational Structure
Activities and Initiatives
- Security Cooperation: Joint anti-terror drills (“Peace Mission”), RATS intelligence sharing, condemned terrorism (e.g. Tianjin Declaration 2025, Pahalgam attack).
- Economic Initiatives: Trade, investment, joint bonds, payment system proposals, infrastructure corridors, and economic councils.
- Connectivity: Transport corridors (N–S, E–W), synergy with Belt & Road (India opposes BRI-CPEC over sovereignty), focus on regional access.
- Cultural Exchanges: Traditional medicine, science, youth empowerment, Buddhist heritage, Varanasi (SCO Tourism Capital 2022–23).
- Recent Summits:
- 23rd Meeting of the SCO Council of Heads of State (CHS) (India, 2023): Iran admitted. India’s “SECURE” priorities.
- 24th Meeting of the SCO Council of Heads of State (CHS) (Astana, 2024): Belarus admitted; focus on diplomacy and Afghanistan.
- 25th Meeting of the SCO Council of Heads of State (CHS) (Tianjin, 2025): Tianjin Declaration, terrorism condemned, future reforms discussed.
Significance for India
- Counter-Terrorism & Security: Addresses India's neighbourhood challenges, RATS intelligence, condemnation of attacks (Tianjin Declaration).
- Central Asia Engagement: Facilitates “Connect Central Asia” policy, access to energy-rich states.
- Energy Security: Cooperation on oil, gas, and proposed pipelines (India-Pakistan-Iran).
- Connectivity & Trade: INSTC, Chabahar corridor, alternatives to BRI, trade access to Eurasia.
- Multilateral Diplomacy: Engages China, Russia, promotes UN reforms, civilisational dialogue, and Varanasi cultural capital.
- Strategic Balance: Simultaneous engagement with China/Russia and Western partners (QUAD), strategic autonomy.
Challenges for India
- China–Pakistan Axis: CPEC through PoK, opposition on sovereignty, frequent coordination by China and Pakistan.
- Balancing Major Powers: Managing ties amid differences (Ukraine, Taiwan) and with Western groupings.
- India–Pakistan Relations: Difficulty in consensus on terrorism, India’s refusal to sign certain statements lacking strong anti-terror language.
- Economic Hurdles: Low trade with Central Asia, connectivity barriers, and visa issues, compared to China’s outreach.
- Ambiguous Mandate: SCO lacks a clear identity; oscillation between security and economic functions, and effectiveness is questioned.
Suggestions & Way Forward
- Strengthen Terror Cooperation: Active use of RATS, push for a unified anti-terror position, zero tolerance.
- Promote Connectivity: Accelerate INSTC, Chabahar, national currency-based settlements, and diversify access routes.
- Economic Engagement: Increase participation in SCO business forums, attract investment, and joint initiatives in digital and green sectors.
- Cultural Diplomacy: Leverage soft power (Buddhism, yoga, Ayurveda), promote youth/science/culture programs.
- Strategic Autonomy: Active participation, balance ties with QUAD/ASEAN, advocate an inclusive, rules-based order.
UPSC Prelims Facts
- Formation: 2001;
- Charter: 2002;
- HQ: Beijing (Secretariat), Tashkent (RATS).
- Members (2025): Belarus, China, India, Iran, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Pakistan, Russia, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan.
- Observers: Afghanistan, Mongolia.
- Dialogue Partners: 14, including Turkey, Sri Lanka, UAE, Qatar, etc..
- Official Languages: Chinese & Russian.
- Permanent Bodies: Secretariat (Beijing), RATS (Tashkent).
UPSC Mains Pointers & Analysis
- Trace evolution from Shanghai Five to 10-member SCO; analyse effects of recent expansion.
- Critically assess “Shanghai Spirit” – is it reflected in practice, especially in decision-making and inclusivity?.
- India’s role: Security, connectivity, energy, trade, soft-power initiatives; cite Varanasi, youth programs.
- Challenges: China-Pakistan collusion, trade constraints, balancing multilateral ties, and the effectiveness of anti-terror platforms.
- Importance of recent summits: Advancement of multipolarity, condemnation of terrorism; assess the impact on regional and Indian interests.
Courses by UPSCprep.com
A comprehensive range of courses meticulously designed to help you cover the syllabus in phases, without overwhelming you with long classes, ensuring you have ample time for self-study.
