Table of contents
The tapestry of ancient India is richly woven with the rise and fall of powerful dynasties.
Understanding these dynasties is not just about memorizing dates and rulers; it's about unlocking the essence of governance, cultural shifts, and the subcontinent's very identity.
This article equips you with a strategic approach to deciphering these historical heavyweights. So, sharpen your swords of knowledge and embark on a conquest of ancient Indian dynasties!
The Mauryan Empire (322 BCE – 185 BCE)
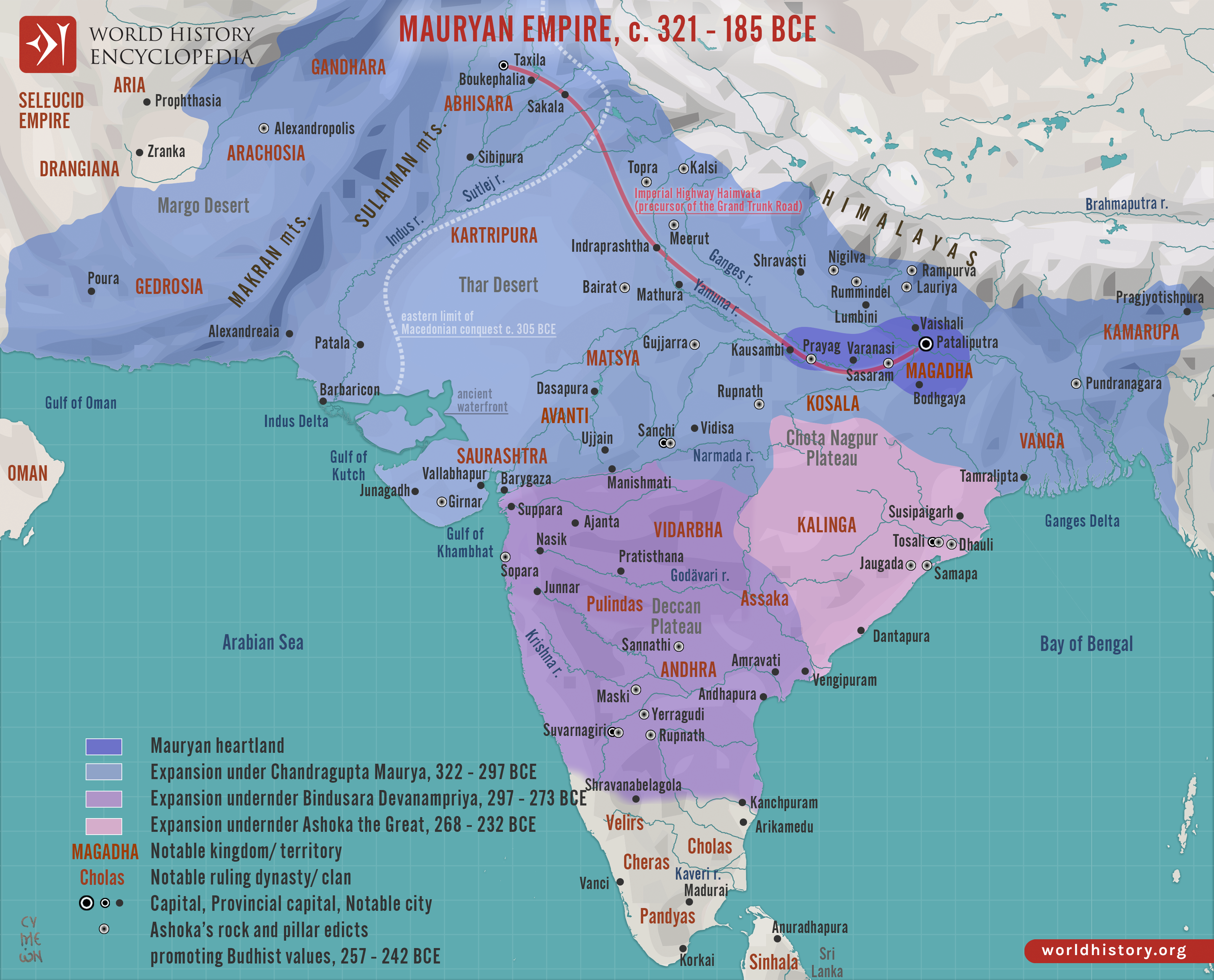


- Chandragupta Maurya was the founder of the Maurya dynasty who defeated Dhanananda, the last ruler of the Nanda dynasty.
- Alexander abandoned Indian conquest and Chandragupta defeated Seleucus Nikator.
- Second ruler was Bindusara, also called Amitraghata or Amitrochates by Greeks who had Deimachus as Greek ambassador.
- Third ruler was Ashoka who is considered India's greatest ruler.
- He was ruthless till 265 BC when the victory in battle of Kalinga changed his heart due to the bloodshed.
- He followed non-violence and embraced and propagated Buddhism.
- Third Buddhist council took place during his time at Pataliputra, presided over by Moggaliputta Tissa, which saw the compilation of Abhidhamma Pitaka.
- To propagate dhamma, Ashoka used edicts and installed 14 major rock edicts across India.
- Written in Prakrit, Aramaic and Greek languages and Brahmi and Kharosthi scripts.
The Gupta Empire (320 CE – 550 CE)
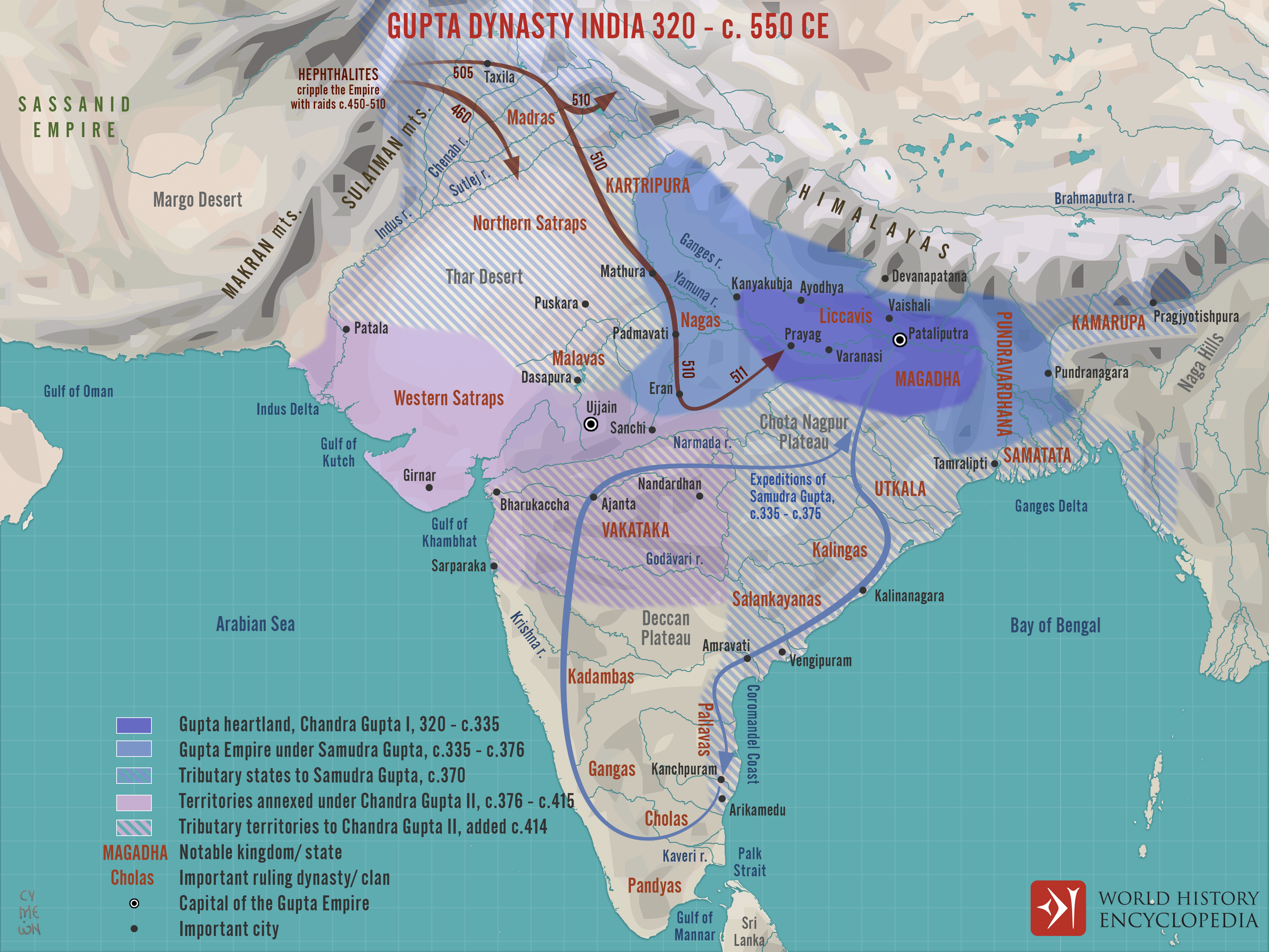

- The Gupta Dynasty ruled a major portion of the Indian subcontinent from the early 4th century CE to the late 6th century CE.
- It was founded by Chandragupta I.
- He assumed the title Maharajadhiraja and issued gold coins.
- Another great ruler was Samudragupta, known as the Napoleon of India, who reigned from 335 AD – 380 AD.
- He also had titles like Vikramanka and Kaviraja.
- Samudragupta’s court poet Harisena wrote Prayag Prashasti which gives an idea about his accession, conquests and subjugation of three Aryavarta kings.
- Chandragupta II or Vikramaditya is one of the greatest rulers of the Gupta dynasty.
- Many inscriptions attributed to him are at Delhi iron pillar, Sanchi and Supiya stone pillar.
- He had navaratnas at his court and Chinese traveler Fa-Hien visited India during his reign.
- Kumaragupta I established Nalanda University and performed Ashvamedha ceremony.

Satavahanas (late 2 BCE to till early 3 CE)

- In the Deccan, the Satavahanas succeeded the Mauryas.
- With Pratishthana and Amaravathi as capital, and were also known as the Andhras.
- Simuka was the founder and is mentioned in the Nanaghat inscription.
- Next ruler was Satakarni I who is described as Dakshina Pathapati in the Naneghat inscription and in Hathigumpha inscription.
- Gautamiputra Satakarni was the greatest ruler with title Kshatriyadarpa Mardana in Nasik inscription and patronized Brahmanism and Buddhism.
- Junagadh inscription states that he was defeated by Rudradaman I.
- Vashishtaputra Pulamayi was the next ruler who is mentioned in Karla Caves' and Junagadh inscriptions.
- He repaired the Amaravati stupa.
- They patronized the Amaravati School of Art and rock-cut architecture and were succeeded by the Ikshvaku dynasty.
Pallavas (275 CE to 897 CE)
- Early Pallavas came to power during the end of Ikshvaku rule in Andhra when Pallava king Simhavarma defeated the Ikshvaku king Rudrapurushadatta in 300 CE and established ”Karmarashtra”.
- Sivaskandavarman was the greatest of the early Pallavas as his dominions extended from Krishna to the South Pennar and up to the Bellary district.
- Nandivarman I was the last ruler of the early Pallava kings as Kalabhras invaded their territories..
- The first ruler of Imperial Pallavas was Simhavishnu (575 – 590 CE) who defeated the Kalabhras.
- Narasimhavarman I was the greatest of the Pallavas with the title Mahamalla or Mamalla (constructed Mamallappuram) who led a naval expedition to Sri Lanka.
- During his reign, Hiuen Tsang visited Kanchi to see that Buddhism and Jainism flourished
- Narasimhavarman II with the title ”Rajasimha‟ constructed Shore temple at Mamallapuram and the Kailasanatha temple at Kanchi.
Chola Dynasty (from 850 CE)
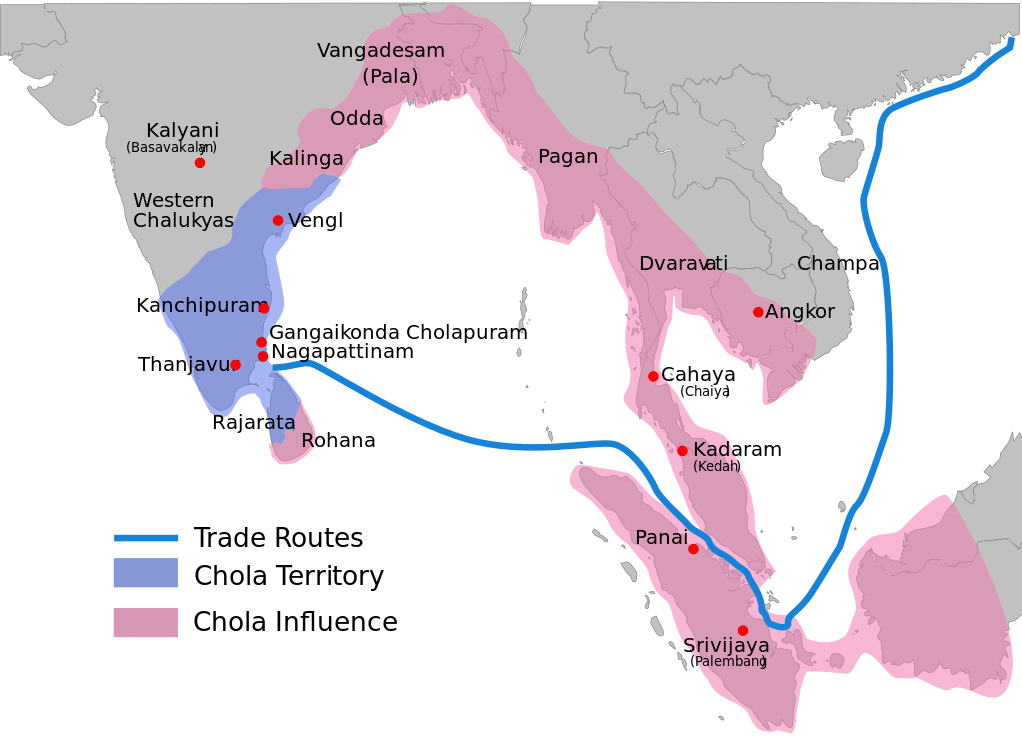

- Vijayalaya founded the Chola kingdom in 850 AD by conquering the Kaveri delta from Muttaraiyar and established the city of Thanjavur.
- Rajaraja I was the most successful Chola king due to his naval expeditions in Sri Lanka and Maldives and victory over Cheras, Western and Eastern Chalukyas.
- He constructed a dam across kaveri river and built Rajarajeswara temple or Brihadeeswara temple at Tanjore
- Next ruler was Rajendra I who defeated Mahipala 1 of Bengal and founded the city of Gangaikondacholapuram and constructed Rameshwaram temple.
- He got the title Kadaramgonda.
- Chola rulers were Saivite and a philosophical system called Saiva Siddhanta was founded.
- Practice of sati became widespread and the Devadasi system started..
- Tamil literature progressed as seen in Kamban Ramayan by Kamban, Periyapuranam or Tiruttondarpuranam by Sekkilar, Kalladam by Kalladanar and Nalavenba by Pugalendi.
