This article covers the 'Major Relief and Geological Features' you must know for the UPSC Civil Services exam, arranged by major regions and continents. Focus on recognising these features on elevation/geological maps and memorising their geographic locations.
Indian Subcontinent Elevation Map

- The Himalayas: World’s highest mountain range; northern boundary of India; influences monsoon and river systems.
- Indo-Gangetic Plains: Vast fertile alluvial plain between the Himalayas and the Deccan plateau, formed by rivers Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra.
- Peninsular Plateau: Ancient, stable landmass; includes Deccan Plateau, Malwa Plateau, Chhota Nagpur Plateau, and Bundelkhand.
- Eastern and Western Ghats: Ranges flanking the Deccan Plateau; the Western Ghats are higher and more continuous.
- Thar Desert: Arid area in northwest India (Rajasthan), formed by rain shadow effect.
- Coastal Plains: Eastern and Western coastal plains along the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea, separated by the Ghats.
- Islands: Andaman & Nicobar (Bay of Bengal), Lakshadweep (Arabian Sea).
Geological Map of India
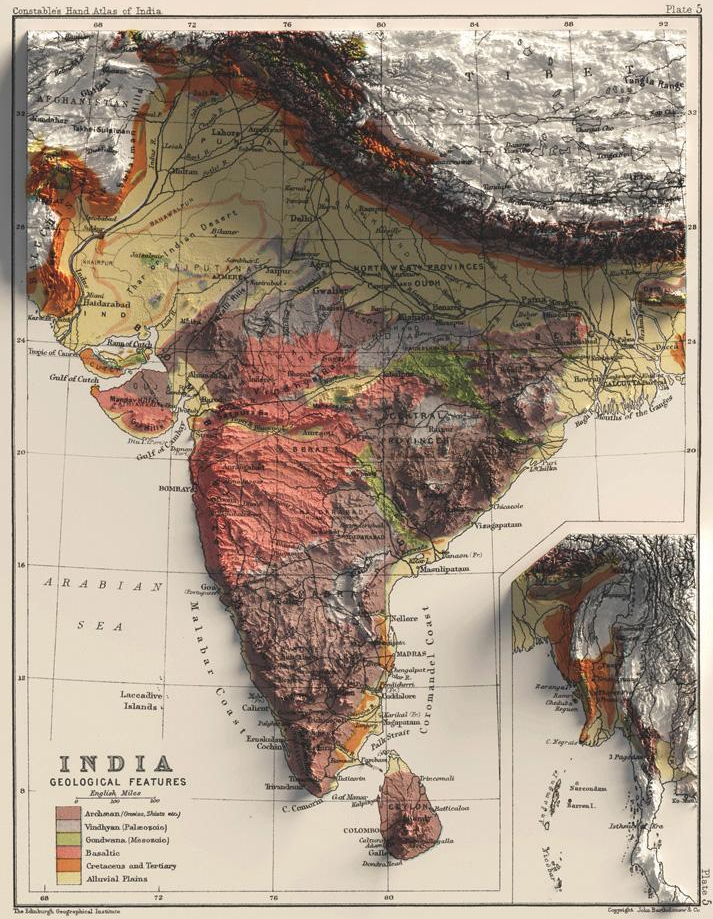
- Deccan Traps: Large volcanic basalt province; among world’s largest; source of black soil.
- Gondwana Rocks: Found in Damodar, Mahanadi, and Godavari basins; significant for coal reserves.
- Vindhyan Systems: Sedimentary rocks, mainly in central India.
- Aravalli Range: Among oldest mountain ranges; regionally significant for mineral resources.
Elevation Map of Asia

- Himalayas: Extends into Nepal, Bhutan, and Pakistan, forming Asia’s roof.
- Tibetan Plateau: "Roof of the World," highest and largest plateau.
- West Siberian Plain: One of world’s largest flatlands, major feature of northern Asia.
- Central Asian Highlands: Steppes (grasslands) and deserts like the Gobi Desert; significant for nomadic cultures.
- Major Rivers: Indus, Ganga, Brahmaputra (South Asia), Yangtze, Yellow (China), Amur, Mekong.
- Deserts: Gobi (Mongolia/China), Karakum, Kyzylkum.
Elevation and Geological Maps of Africa

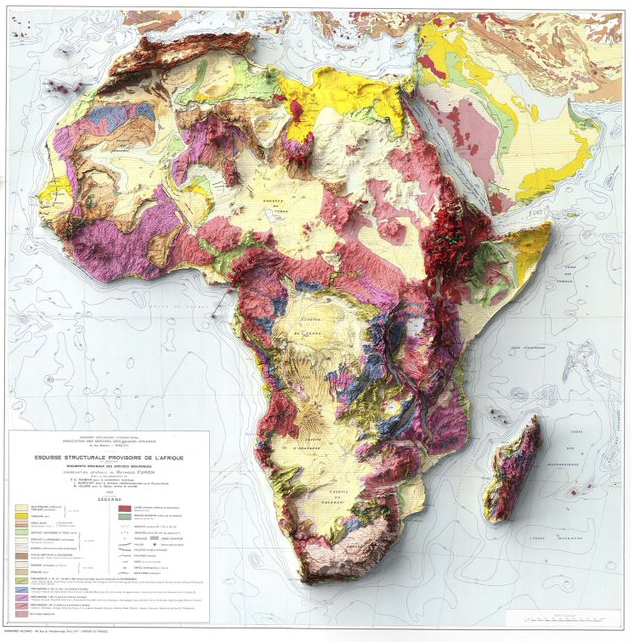
- Plateaus: Most of Africa is a series of plateaus at different elevations (average 600m), not long continuous mountain chains.
- Ethiopian Highlands: Highest, most rugged; elevations over 4,400m.
- East African Rift: Great East African Rift Valley, with volcanic peaks: Mt. Kilimanjaro (Africa’s highest), Mt. Kenya, Rwenzori Mountains.
- Great Basin Areas: Congo, Chad, Kalahari, and Sudan basins.
- Deserts: Sahara (North), Kalahari (Southwest), Namib (West coast).
- Rivers: Nile (world’s longest), Congo, Niger, Zambezi.
Geological Map of Australia
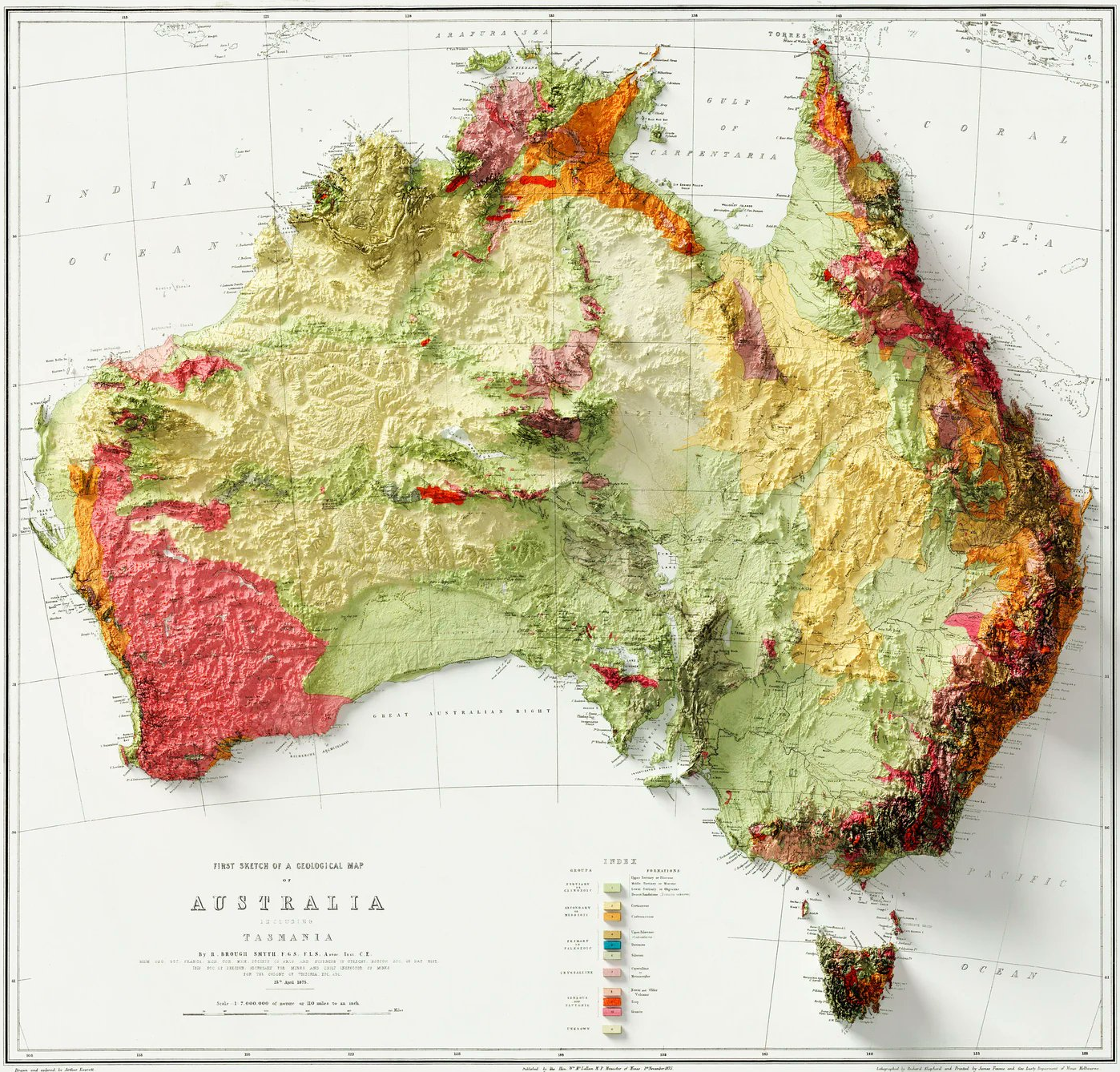
- Western Plateau: Ancient, stable cratonic region with features like Yilgarn and Pilbara cratons; arid, flat.
- Great Dividing Range: Runs parallel to the East Coast, separates rivers draining east and west.
- Eastern Highlands: Includes the Blue Mountains, Victorian Alps, Mount Kosciuszko (highest point).
- Uluru and Kata Tjuta: Famous inselbergs (isolated rocky hills).
- Central Lowlands: Lake Eyre basin—very flat; arid.
- Coastal Plains: Relatively narrow except in the north.
Geological Map of Europe

- East European (Russian) Plain: Broad, flat, extending from Russia to Central Europe.
- Scandinavian Highlands: Rugged, fjorded.
- Alpine System: Pyrenees, Alps, Carpathians, Apennines, Balkan Mountains—form the major mountain backbone, separating North and South Europe.
- Ural Mountains: Eastern boundary of Europe, separates Europe from Asia.
- Iberian and Italian Peninsulas: Varied, mountainous relief.
Geological Map of North America
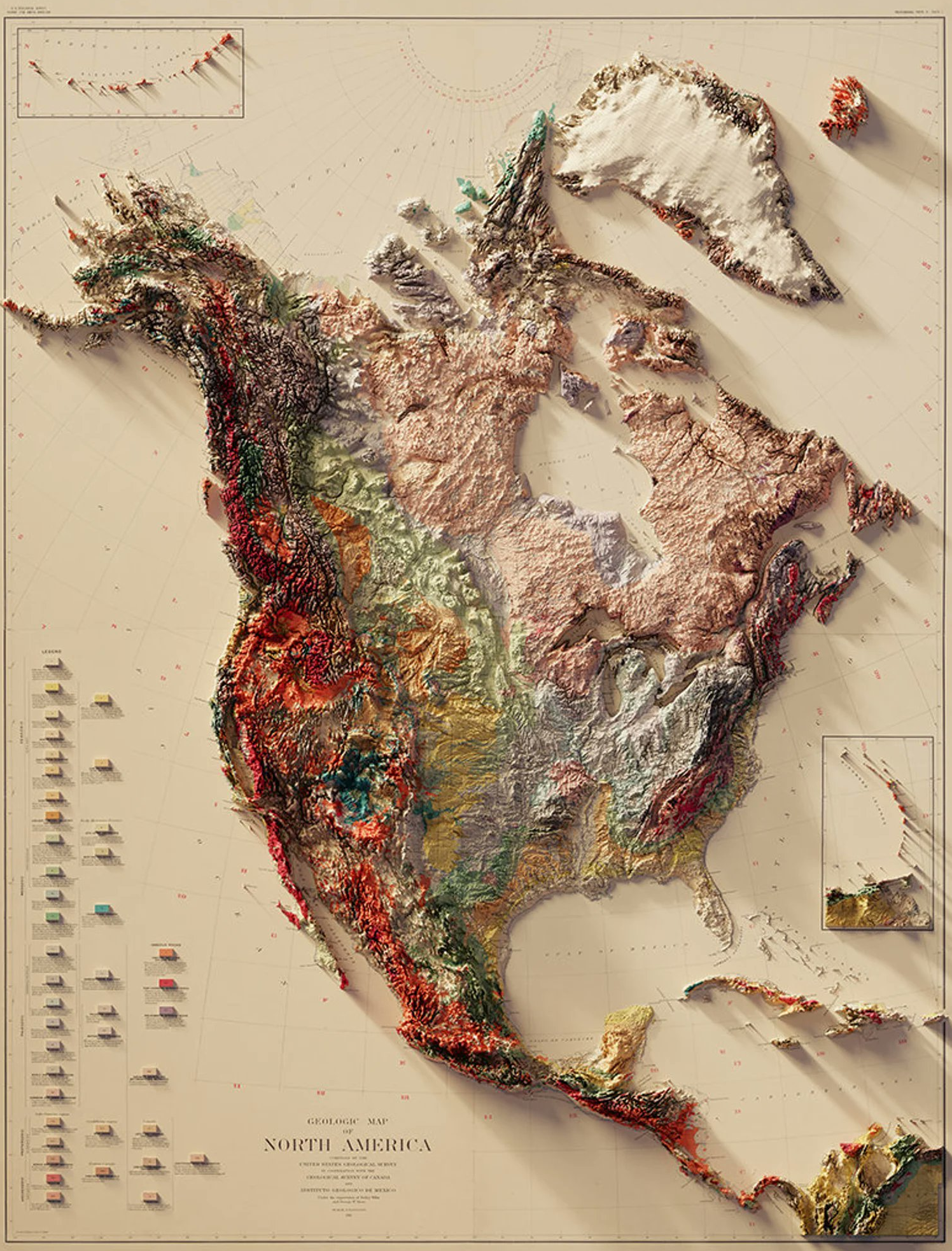
- Canadian Shield: Exposed Precambrian rocks in eastern/northern Canada; source of mineral resources.
- Appalachian Mountains: Ancient, eroded range in the east.
- Interior Plains: Broad, low plains (Great Plains, Central Lowlands).
- Rocky Mountains: Major mountain range of western North America.
- Cordillera: Comprehensive term for all mountainous west; includes Cascades, Sierra Nevada.
- Coastal Plains: Atlantic and Gulf coastal lands.
- Colorado Plateau: Uplifted, deeply eroded with canyons including Grand Canyon.
Geological Map of South America
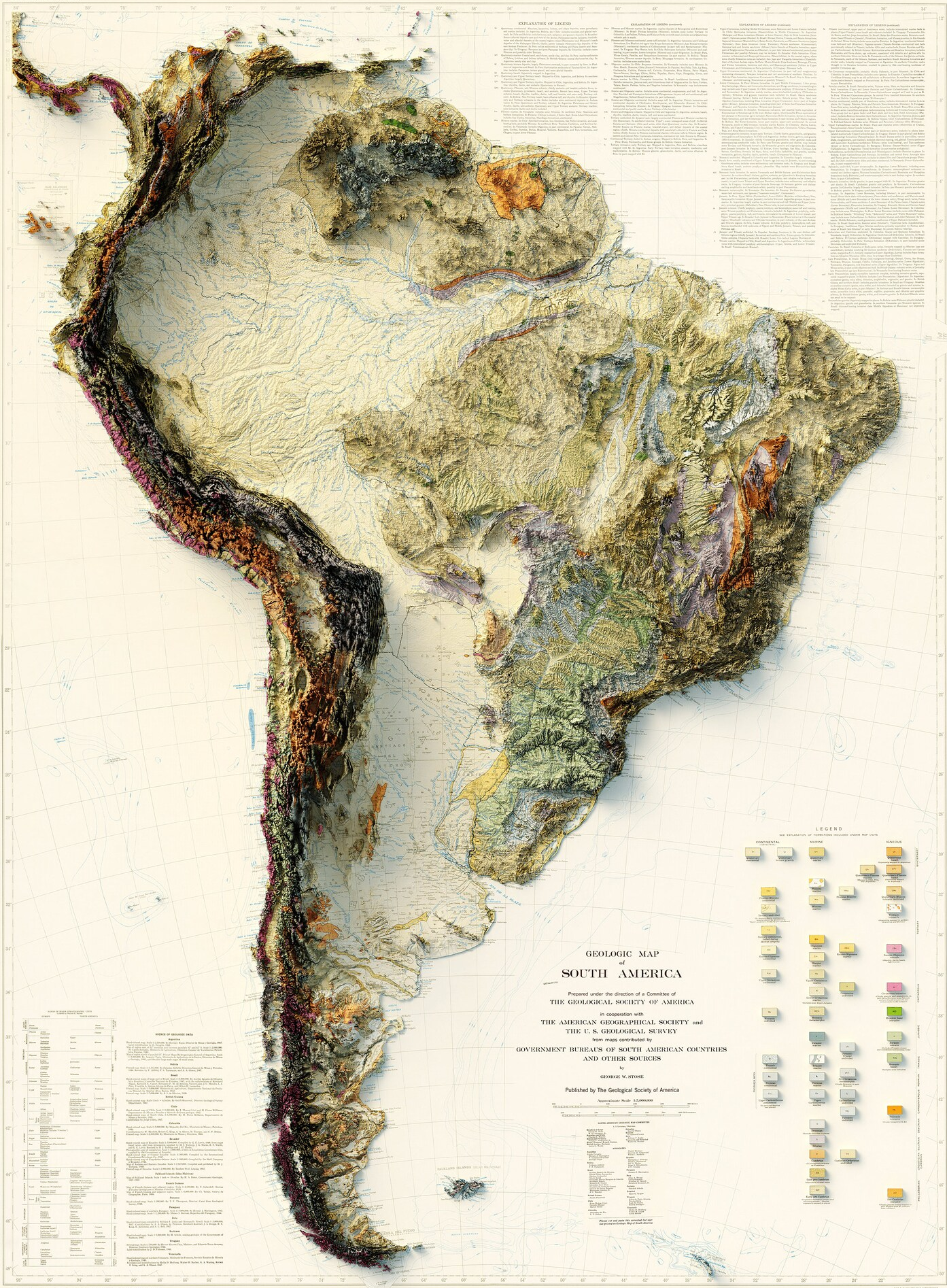
- Andes Mountains: World’s longest continental mountain chain, continuous along the western edge, includes highest peaks outside Asia like Aconcagua.
- Brazilian and Guiana Highlands: Precambrian uplands in the east and north, dissected by major rivers.
- Amazon Basin: World’s largest rainforest, flat, low-lying.
- Orinoco and Paraná Basins: Other important lowland areas.
- Patagonia: Arid plateau in the south.
- Atacama Desert: Driest place on earth, northern Chile.
Elevation Map of Antarctica

- Transantarctic Mountains: Divide continent into East and West Antarctica (East: mostly high plateau; West: lower and mountainous).
- Antarctic Peninsula: Northward extension toward South America.
- Ice Sheet: Over 98% of the continent is covered by thick ice; highest average elevation of all continents.
Key Global Relief Features
| Region | Mountains/Highs | Plateaus/Plains | Basins/Lows | Deserts | Special Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indian Subcontinent | Himalayas, Western/Eastern Ghats | Peninsular, Deccan, Chhota Nagpur | Indo-Gangetic Plain | Thar | Islands: Andaman, Lakshadweep |
| Asia | Himalayas, Hindu Kush | Tibetan Plateau, Steppes | Ganga, Indus, Brahmaputra Plains | Gobi, Taklamakan | Lake Baikal, Aral Sea |
| Africa | Ethiopian Highlands, Rwenzori | East, Southern African Plateaus | Chad, Congo Basins | Sahara, Kalahari, Namib | Rift Valley, Kilimanjaro |
| Australia | Great Dividing Range | Western Plateau, Arnhem Land | Central Lowlands | Great Victoria, Simpson | Uluru (Ayers Rock) |
| Europe | Alps, Carpathians | East European Plain | Po, Danube Basins | None major | Scandinavian Fjords |
| North America | Rockies, Appalachians | Canadian Shield, Great Plains | Mississippi Basin | Mojave, Sonoran | Colorado Plateau, Great Lakes |
| South America | Andes | Brazilian, Guiana Highlands | Amazon, Orinoco Basins | Atacama, Patagonian | Lake Titicaca, Pampas |
| Antarctica | Transantarctic Mountains | East Antarctic Plateau | N/A | N/A | Ice Sheet, Antarctic Peninsula |
Tip for UPSC:
Focus on location, geologic history, and significance of each feature—these often serve as map-based and comparative geography questions in both prelims and mains.
Courses by UPSCprep.com
A comprehensive range of courses meticulously designed to help you cover the syllabus in phases, without overwhelming you with long classes, ensuring you have ample time for self-study.
