Table of contents
The fight against climate change and environmental degradation demands global cooperation.
Understanding key environmental conventions is crucial for UPSC aspirants. This section provides a concise overview of these agreements, empowering you to stay informed and contribute to a sustainable future.
CITES
Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species


- CITES was formed in response to a decision by the International Union for Conservation of Nature in 1963.
- There are 184 parties as members to ensure the survival of wild animals and plants is not endangered by their international trade.
- The United Nations Environment Programme is the body for running the CITES Secretariat located in Geneva, Switzerland.
- It is a binding agreement between the Parties with national laws still applying.
- The Conference of the Parties to CITES is the highest decision-making body.
Convention on Migratory Species


- Also called the Bonn Convention or the Convention of Migratory Species of Wild Animals.
- CMS is the only treaty that addresses protection of wild-caught migratory species which are around 173 in number.
- The Convention has two appendices viz Appendix I in which migratory species that are endangered or threatened with extinction are listed and Appendix II in which unfavorable conservation status species are listed which require international agreements for their conservation.
- States are responsible for safeguarding any species that reside inside or pass through their territorial or legal authority.
Ramsar Convention


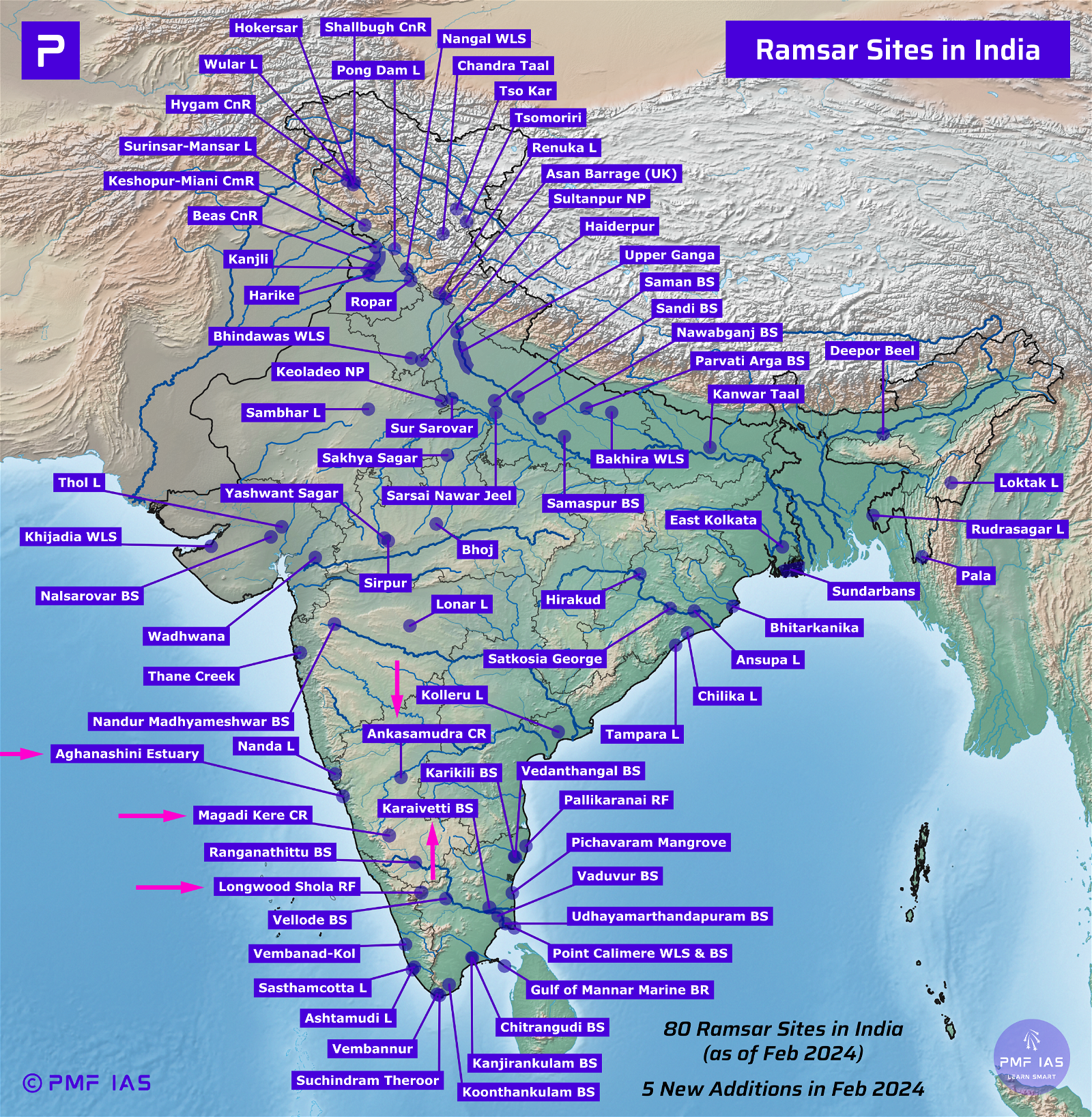
- Ramsar Convention on Wetlands was signed in 1971 in the Iranian city of Ramsar.
- The aim of the convention is global sustainable development by conserving and wisely using all wetlands.
- Montreux Record is a list of wetlands where ecological characteristics have changed, are changing, or are likely to change due to human activity.
- Loktak Lake and Keoladeo National Park are the only two wetlands from India to appear in the Montreux Record.
Global Tiger Forum


- It is the only intergovernmental organization with willing nations as members to safeguard the tiger.
- It aims to protect the world's remaining six subspecies of tigers in 14 countries, including the Bengal, Amur, South China, Sumatran, Indochinese, and Malayan.
- It was established in 1994 with headquarters in New Delhi.
- The tiger, as an apex predator, is a symbol for the preservation of all species and the health of our ecosystem.

UNCCD
United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification


- UNCCD is the only body that addresses the causes and impacts of desertification and drought.
- Also, it is the only legally binding international agreement that connects the environment, sustainable land management and development.
- UNCCD along with the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change and the Convention on Biological Diversity is one of three Rio Conventions.
- India at COP14 announced restoration of 5 million hectares of degraded land by 2030, bringing the total amount of land to be restored in India to 26 million hectares.
UNFCCC
United Nations Framework Convention On Climate Change


- It is a global environmental pact addressing climate change enforced after the Rio Earth Summit 1992 (UN Conference on Environment and Development).
- Its objectives are to keep atmospheric greenhouse gas at a level that avoids harmful impact on the climate system.
- The UNFCCC Climate-Tech Centre Network serves as the operational arm and promotes technology transfer for low-carbon and climate-resilient development.
- Parties to the UNFCCC are categorized into Annex I, Annex II, Annex B, Least-developed countries and Non Annex countries.
Paris Agreement


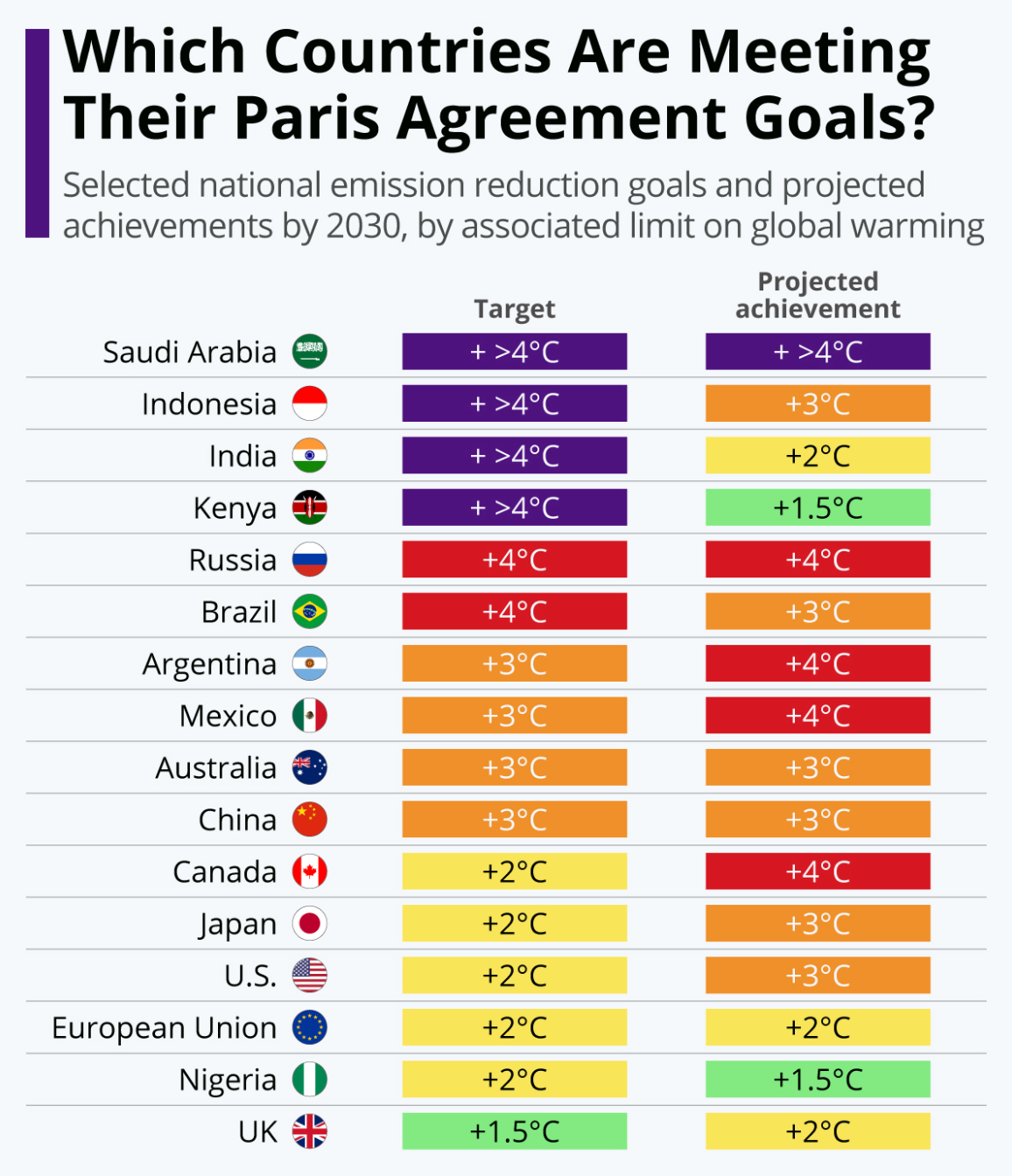
- The Paris Agreement is a pivotal global accord adopted in 2015 during the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) COP21 meeting in Paris, France.
- The agreement seeks to strengthen the global response to climate change by limiting the global temperature rise this century to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, with efforts to limit the increase even further to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
- The Paris Agreement emphasizes the need for global cooperation, encouraging countries to submit nationally determined contributions (NDCs) outlining their climate action plans, and to regularly review and enhance these commitments to achieve the long-term goals.
UNCBD
United Nations Convention On Biodiversity

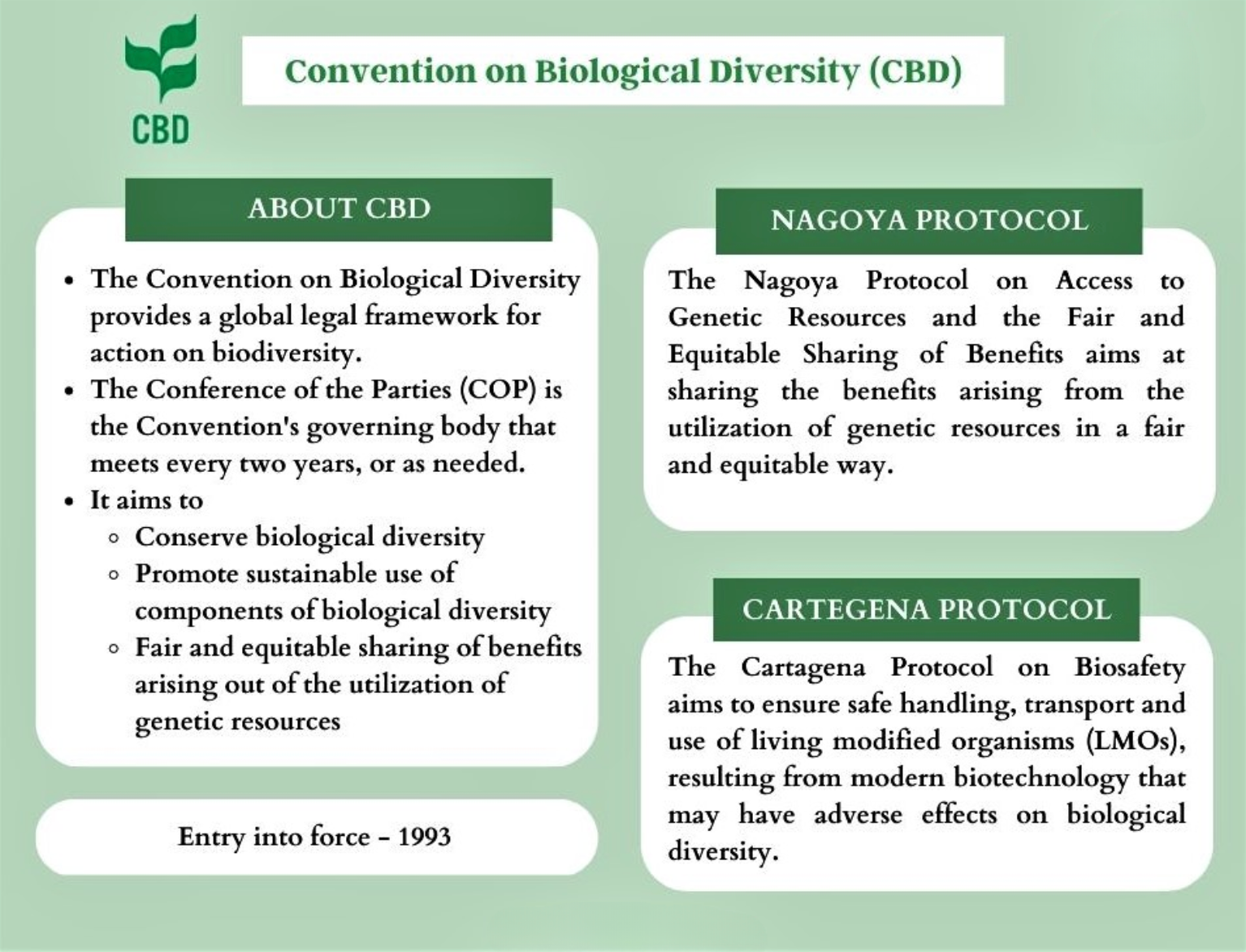
- UNCBD was also adopted in the 1992 Rio de Janeiro Earth Summit with the secretariat in Montreal, Canada.
- It acknowledged for the first time that humankind shares a concern for biological diversity conservation.
- The objectives include preservation of biological diversity, sustainable utilization of biological resources and fair and equal sharing of gains from the utilization of genetic resources.
- India passed the “Biological Diversity Act '' in 2002 to enforce the CBD’s mandate.
Kyoto Protocol

- The Kyoto Protocol was enforced to make the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change operative by requiring developed nations and transition economies to set their own individual emission targets for greenhouse gasses.
- It introduced the principle of "common but differentiated responsibility and respective capabilities," to bind the developed nations because they are mostly responsible for the high levels of GHG emissions.
- It was approved in 1997 at COP3 of the UNFCCC in Kyoto, Japan but enforced in 2005.
- From 2008 to 2012 i.e the first commitment period, it aimed to reduce GHG emissions in the developed countries by approximately 5% by 2012 compared to 1990 levels.
- The Kyoto Protocol is applicable only for the six GHGs mentioned in Annex A.
Kigali Agreement
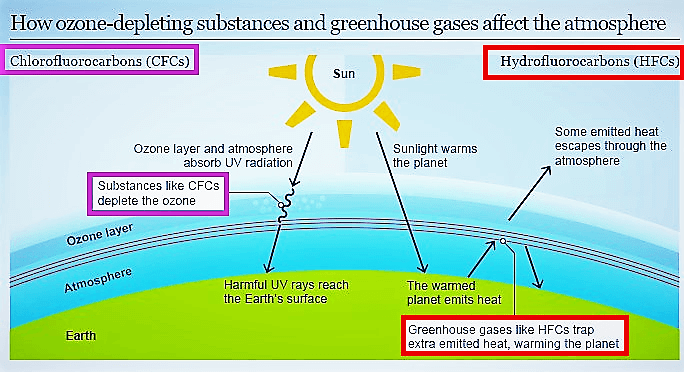

- The Kigali agreement was held in Rwanda to amend the 1987 Montreal Protocol for phasing out hydrofluorocarbons.
- The Montreal Protocol was for removal of ozone-depleting substances but the Kigali agreement acknowledges their role in global warming also.
- HFCs break down in the troposphere, react with hydroxyl radicals to split and trap the solar radiation (infrared radiation) re-directing it toward Earth's surface.
- The Montreal Protocol was amended several times and the 8th amendment is the Kigali Amendment.
- The signatories have to reduce production and use of hydrofluorocarbons by 80-85 percent from their baseline levels by 2045.
Nagoya Protocol

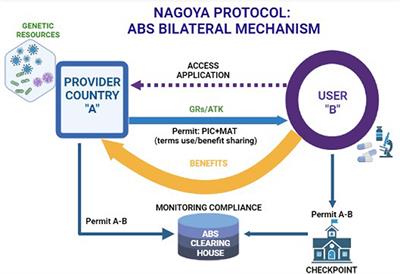
- This protocol is based on Access to Genetic Resources and the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits arising from their Utilization.
- It is an addition to the UN Convention on Biological Diversity and the protocol provides the legal foundation for its implementation.
- The Nagoya Protocol has been ratified by 137 parties as of 2022 including India.
- It aims to provide fair and non-arbitrary rules, establish clear rules for prior informed consent, encourage research for biodiversity conservation and give due consideration to cases of conflicts.
- The Nagoya Protocol and the Strategic Plan for Biodiversity 2011-2020 was a ten-year plan and its result was the Aichi Targets for biodiversity.
Stockholm Convention

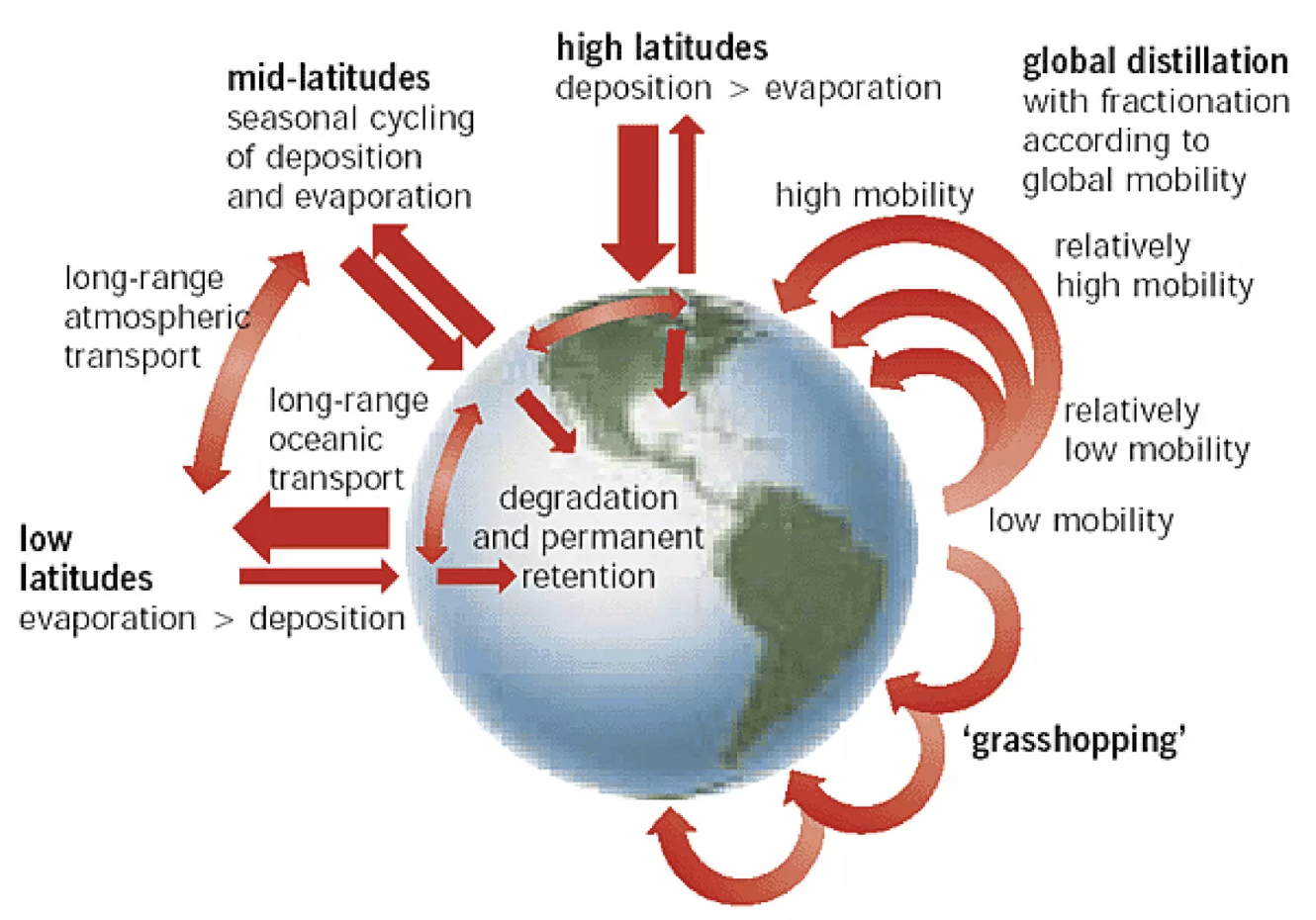
- The Stockholm Convention on persistent organic pollutants aims to prevent or limit the usage of persistent organic pollutants.
- They are hazardous substances composed of organic (carbon-based) chemical compounds like DDT, polychlorinated biphenyls and unintended byproducts like dioxins.
- POPs are not soluble in water but are absorbed in fatty tissues.
- List of POPs include Aldrin, Chlordane, Heptachlor, Hexachlorobenzene, DDT, Dieldrin, Endrin, Mirex and Toxaphene (pesticides), Hexachlorobenzene and Polychlorinated biphenyls (Industrial Chemicals) and Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and Polychlorinated dibenzofurans (by products)
Basel Convention


- Basel Convention is on the control of transboundary movements of hazardous wastes and their disposal.
- It aims to stop the movement of hazardous waste across countries, especially from more developed to less developed ones, but the treaty does not regulate the transportation of radioactive waste.
- The increased public opposition to hazardous waste dumping, known as the NIMBY (Not In My Back Yard) syndrome and increase in disposal costs led to this convention.
- Also, the Khian Sea waste disposal incident, in which a ship carrying incinerator ash from Philadelphia dropped half of its load on a Haitian beach, was one of the events that prompted the Basel Convention.
Rotterdam Convention


- The Rotterdam Convention was adopted in Rotterdam (Netherlands) to promote shared responsibility with respect to the global trade of hazardous chemicals.
- The Prior Informed Consent procedure is implemented under it for obligatory legal responsibilities.
- The parties must legally obtain and communicate the receipt of future shipments of the substances listed in Annex III of the Convention before their import.
- There is a decision guidance document that provides all the details about the substances in Annex III, which contains 52 chemicals, 35 pesticides, 16 industrial chemicals, and one chemical which is both pesticide and an industrial chemical.
Montreal Protocol


- The Montreal Protocol is a landmark international treaty adopted in 1987, aimed at protecting the ozone layer by phasing out the production and consumption of nearly 100 man-made chemicals known as ozone-depleting substances (ODS).
- These substances include chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), halons, and other related chemicals that are responsible for ozone depletion.
- The Protocol is considered one of the most successful environmental agreements to date, with significant reductions in ODS and a positive impact on the recovery of the ozone layer.
Let's Revise