About:
- Founded in 1999 after the Asian financial crisis
- Initially started off as a meeting of finance ministers and central bank governors.
- As a response to the financial crisis of 2008, the G-20 was upgraded to head of state level in an inaugural summit in Washington, D.C.
- It is also known as the “Summit on Financial Markets and the World Economy” and represents 80% of the global GDP.
- G-20 operates without a permanent secretariat or staff
- Groups chair rotates annually among member countries
- India will host first summit of G-20 in 2022.
- Chiefs of IMF, WB, and other imp people participate in G 20 Summit
- G20 nations collectively account for 78% of all emissions. (Emission Gap Report, UNEP)
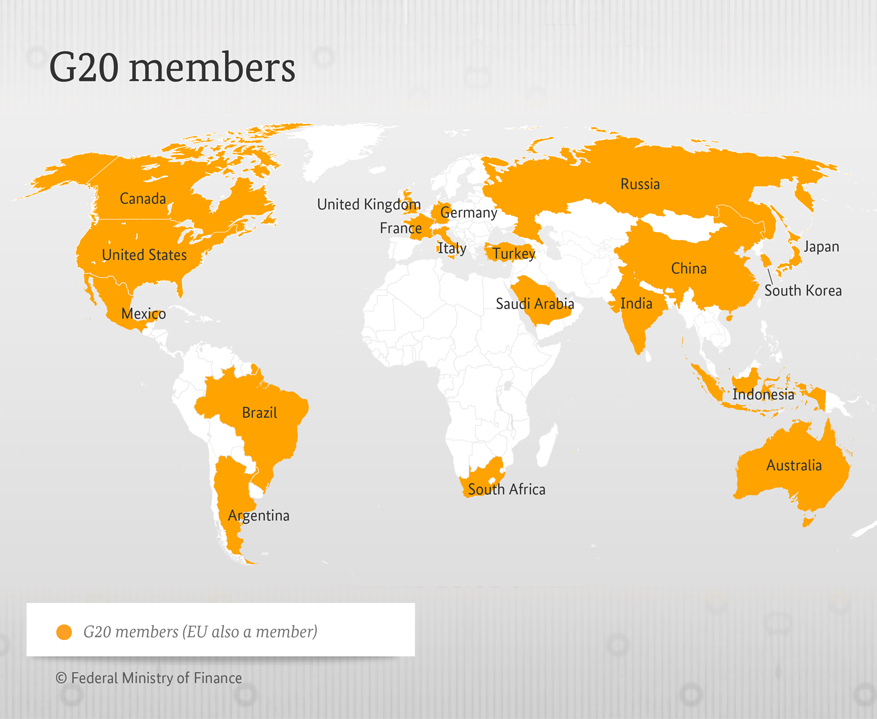
Member Countries
Mnemonic to remember G20 Countries: GURU JI SITA AB SSC FCI ME kaam karti hain
- G - Germany
- U - USA
- R - Russia
- U - UK
- J - Japan
- I - India
- S - S. Africa
- I - Italy
- T - Turkey
- A - Argentina
- A - Australia
- B - Brazil
- S - Saudi Arabia
- S - S. Korea
- C - Canada
India's G-20 Presidency
India has been a member of the G20 since its inception in 1999, and it has been actively participating in its meetings to discuss and coordinate policies on various global economic and financial issues, such as trade, investment, climate change, energy, and development.
When India holds the G20 presidency, it gets an opportunity to shape the agenda of the forum and steer the discussions towards issues that are important to its national interests. This can lead to several benefits for India, including:
- Increased visibility on the global stage: As the host of the G20 summit, India will receive global attention and media coverage, which can help raise its profile and enhance its soft power.
- A platform to advocate for its interests: India can use the G20 presidency to promote its economic and strategic priorities, such as job creation, infrastructure development, renewable energy, and digitalization.
- Enhanced economic cooperation: The G20 presidency can help India deepen its economic engagement with other major economies, such as the US, China, and Japan, through bilateral meetings and discussions on trade and investment.
- Addressing global challenges: As a member of the G20, India has a stake in addressing global challenges such as climate change, poverty reduction, and health crises. Through its presidency, India can take a leadership role in shaping the G20's response to these issues.
Overall, the G20 presidency offers India a unique opportunity to shape the global economic agenda and promote its national interests. By leveraging this platform, India can enhance its economic and strategic ties with other major economies and play a more active role in addressing global challenges.
The Financial Stability Board is an international body that monitors and makes recommendations about the global financial system. It was established after the G20 London summit in April 2009 as a successor to the Financial Stability Forum.
Previous Post