Table of contents
World Economic Forum (WEF)
International Organization for Public-Private Cooperation which holds annual gatherings of the world’s most influential business and political decision-makers.
- Established in 1971 as a not-for-profit foundation
- HQ: Geneva, Switzerland.
- It is a membership-based organization, and membership is made up of the world’s largest corporations.
- The Forum provides a platform for the CEOs of the largest companies, heads of state of countries, to meet each other and discuss business through bilateral meetings
Reports released by WEF
- Global Gender Gap Report
- Global Risks Report
- Regional Risks for Doing Business report
- Global Competitiveness Report
- Future of Jobs 2018
- Energy Transition Index
- Global Human Capital Index
- Social Mobility Report
Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO)
FAO was established in 1945 with the objective of eliminating hunger and improving nutrition standards by increasing agricultural productivity.
Secretariat: Rome, Italy.
Recent Developments
- The 160th session of the FAO Council has approved India’s membership to the Executive Board of the United Nations World Food Program (WFP) for 2020 and 2021.
- It also approved India’s proposal to observe an International Year of Millets in 2023.The international endorsement comes in the backdrop of India celebrating 2018 as the National Year of Millets.
- WFP – It was established in 1961 as an experiment to provide food aid through the UN system.It is a member of the United Nations Development Group.
Global Important Agricultural Heritage systems (GIAHS)
- These are outstanding landscapes of aesthetic beauty that combine agricultural biodiversity and ecosystem and valuable cultural heritage.
- Designated by the FAO.
The proposed GIAHS sites are generally assessed based on
- Food and livelihood security
- Agro-biodiversity
- Local and Traditional Knowledge systems
- Cultures, Value systems, and Social Organisations
- Landscapes and Seascapes Features
World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE)
It is the intergovernmental organisation responsible for improving animal health worldwide.
- It is recognised as a reference organisation by the World Trade Organization (WTO).
- It gather and disseminate information about animal diseases around the world and to create health standards to protect international trade in animals and their products. It was founded in 1924.
- HQ - Paris
International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA)
It is an intergovernmental organisation mandated to facilitate cooperation, advance knowledge, and promote the adoption and sustainable use of renewable energy.
- It is the first international organisation to focus exclusively on renewable energy, addressing needs in both industrialized and developing countries.
- It was founded in 2009
- HQ: Masdar City, Abu Dhabi.
- official UN observer.
International Energy Agency
A candidate country must be a member country of the OECD. However, membership in the OECD does not automatically result in membership in the IEA.The IEA is made up of 30 member countries.
International Atomic Energy Agency
- Widely known as the world’s “Atoms for Peace and Development” organization
- It works to promote safe, secure and peaceful use of nuclear technologies.
- Headquarters is in Vienna, Austria.
- It is an independent international organization that reports annually to the UN General Assembly
Arctic Council
- Recently, India was re-elected as an Observer
- Established by the eight Arctic States through the Ottawa Declaration of 1996
- Canada, Denmark (including Greenland and the Faroe Islands), Norway, Sweden, Finland, Iceland, Russia and the United States
- It is not a formalized treaty-based international legal entity and does not allocate resources.
- leading intergovernmental forums, for discussing issues concerning the Arctic region
- decision-making through consensus between the permanent members
- Council does not prohibit the commercial exploitation of resources in the Arctic.
Group of 7 (G-7)
- Informal bloc of 7 industrialized democracies
- The European Union has participated fully in the G-7 since 1981 as a "non enumerated" member. (Represented by President of European Council)
- While the G-7 mainly has to do with politics, the G-20 is a broader group that focuses on the global economy.
- declarations at the end of the summit are not binding.
Mnemonic: JUICE GF
- J- Japan
- U- USA
- I- Italy
- C- Canada (No China)
- E- England
- G- Germany
- F- France
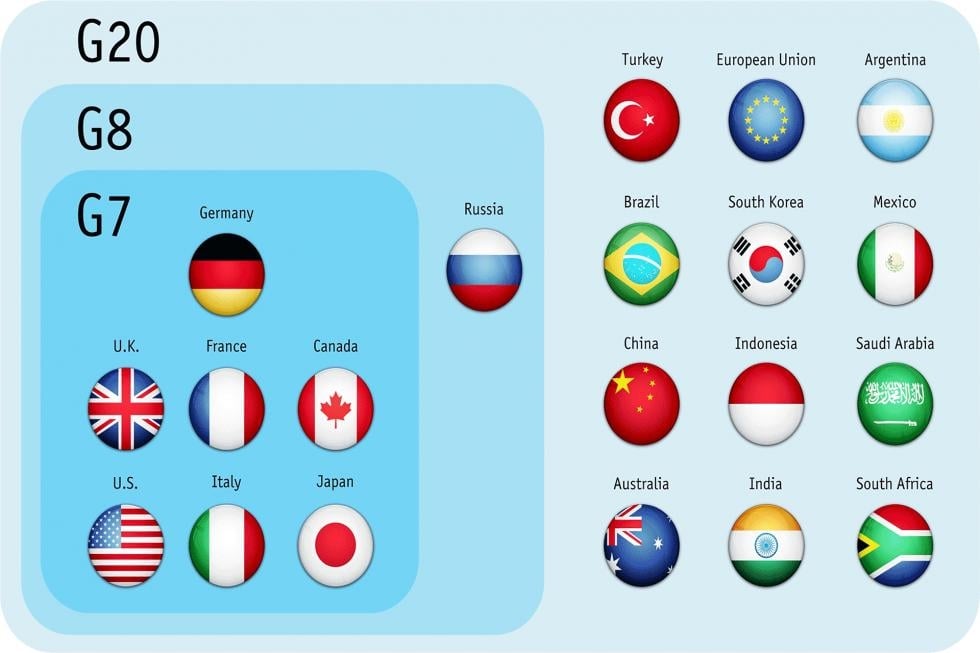
G-20
- Founded in 1999 after the Asian financial crisis
- Initially started off as a meeting of finance ministers and central bank governors.
- As a response to the financial crisis of 2008, the G-20 was upgraded to head of state level in an inaugural summit in Washington, D.C.
- It is also known as the “Summit on Financial Markets and the World Economy” and represents 80% of the global GDP.
- G-20 operates without a permanent secretariat or staff
- Groups chair rotates annually among member countries
- India will host first summit of G-20 in 2022.
- Chiefs of IMF, WB, and other imp people participate in G 20 Summit
- G20 nations collectively account for 78% of all emissions. (Emission Gap Report, UNEP)
Countries: GURU JI SITA AB SSC FCI ME kaam karti hain
The Financial Stability Board is an international body that monitors and makes recommendations about the global financial system. It was established after the G20 London summit in April 2009 as a successor to the Financial Stability Forum.
International Solar Alliance
International Solar Alliance (ISA) is conceived as a coalition of solar resource rich countries to address their special energy needs and will provide a platform to collaborate on addressing the identified gaps through a common, agreed approach.
About ISA
- It is an Indian initiative that was launched by the PM of India and the President of France in 2015 in Paris, on the side-lines of the COP-21, with 121 solar resource-rich countries lying fully or partially between the tropic of Cancer and tropic of Capricorn as prospective members (sunshine countries).
- HQ- Gurugram
- dedicated to the promotion of solar energy
- ISA brings together countries with rich solar potential to aggregate global demand, thereby reducing prices through bulk purchase, facilitating the deployment of existing solar technologies at scale, and promoting collaborative solar R&D and capacity building.
Recent Developments
- In the wake of the global pandemic, ISA responded by setting up ISA CARES (like PM-CARES in India), an initiative dedicated to the deployment of solar energy in the healthcare sector.
- The initiative aims to solarize one primary health Center in each district of the target member countries
- “One Sun, One World, One Grid” Initiative to harness the power of interconnected grids for enabling energy transition to a low-carbon world.
- Solar Risk Mitigation Initiative (SRMI)
- The first project under the SRMI is being launched in Mozambique with the support of France and the European Union (EU).
- Solar awards—
- The Visvesvaraya award recognises the countries with a maximum floating solar capacity in each of the four regions of ISA
- The Kalpana Chawla award for outstanding contribution of scientists and engineers working in the field of solar energy.
- The Diwakar award recognises organisations and institutions that have been working for the benefit of differently-abled people and have maximised the use of solar energy in the host country.
Personal mentorship with crisp content!
Prelims 360 + Mentorship
International Seabed Authority (ISA)
- ISA is an autonomous international organization established under the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
- ISA is the organization through which States Parties to UNCLOS organize and control all mineral-resources-related activities in the Area for the benefit of mankind as a whole.
- In so doing, ISA has the mandate to ensure the effective protection of the marine environment from harmful effects that may arise from deep-seabed related activities.
- HQ in Kingston, Jamaica
- All States Parties to UNCLOS are ipso facto members of ISA.
- It has the observer status to the United Nations.
- India is a member of Council of ISA.
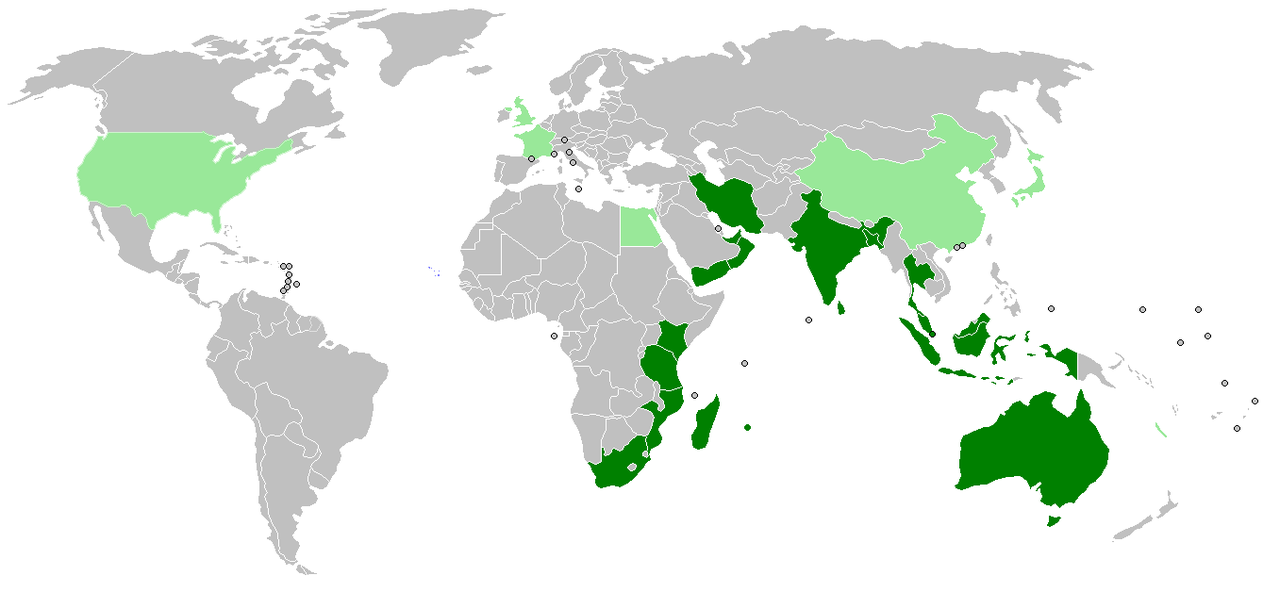
Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA)
- Apex body: Council of Foreign Ministers (COM) which meets annually.
- Secretariat: hosted by the Republic of Mauritius
- The IORA is a regional forum, tripartite in nature, bringing together representatives of Government, Business and Academia, for promoting co-operation and closer interaction among them. It is based on the principles of Open Regionalism for strengthening Economic Cooperation particularly on Trade Facilitation and Investment, Promotion as well as Social Development of the region.
Members
- Australia,
- Bangladesh,
- Comoros,
- India,
- Indonesia,
- Iran,
- Kenya,
- Madagascar,
- Malaysia,
- Mauritius,
- Mozambique,
- Oman,
- Seychelles,
- Singapore,
- Somalia
- South Africa,
- Sri Lanka,
- Tanzania,
- Thailand,
- United Arab Emirates
- Yemen and
- Maldives
Indian Ocean Commission (IOC)
- Recently, India has been approved as an observer state for the Indian Ocean Commission (IOC).
- It is an intergovernmental organization
- It is composed of five African Indian Ocean nations: Comoros, Madagascar, Mauritius, Réunion (an overseas region of France), and Seychelles.
- Mandate: To serve as platform of solidarity for the entire population of the African Indian Ocean region.
Indian Ocean Naval Symposium
The ‘Indian Ocean Naval Symposium’ (IONS) is a voluntary initiative that seeks to increase maritime co-operation among navies of the littoral states of the Indian Ocean Region by providing an open and inclusive forum for discussion of regionally relevant maritime issues.
The 24 member nations of the IONS are grouped into four sub-regions
Alliance of Small Island States (AOSIS)
- It is an intergovernmental organization of low-lying coastal and small island countries.
- The main purpose of the alliance is to consolidate the voices of Small Island Developing States (SIDS) to address global warming.
- AOSIS partners with UNDP to effectively influence climate negotiations.
World Design Organization (WDO)
(formerly known as the International Council of Societies of Industrial Design (ICSID))
- International NGO
- It advocates design for a better World.
- It aims to promote and share knowledge of industrial design-driven innovation that enhances the economic, social, cultural, and environmental quality of life.
- World Design Capital is designated every two years by the WDO. It recognizes cities for their effective use of design to drive economic, social, cultural, and environmental development.
Eastern Economic Forum (EEF)
- It takes place each year in Vladivostok
- established by the decree of the President of the Russia
- It serves as a platform for the discussion of key issues in the world economy, regional integration, and the development of new industrial and technological sectors, as well as of the global challenges facing Russia and other nations.
International Organisation for Migration
- In 2016, IOM became the organisation related to UN
- It was formed after WW2 to resettle refugees
- IOM is dedicated to promoting humane and orderly migration for the benefit of all.
- It does so by providing services and advice to governments and migrants.
- IOM works to help ensure the orderly and humane management of migration,
- to promote international cooperation on migration issues,
- to assist in the search for practical solutions to migration problems and
- To provide humanitarian assistance to migrants in need, including refugees and internally displaced people.
- India is member
- Report: Global migration report.
Interpol
- Interpol is the world’s largest international police organization. It enables cross-border police cooperation, and supports and assists all organisations, authorities and services whose mission is to prevent or combat international crime.
Objectives
- to facilitate international police co-operation even where diplomatic relations are not present between certain countries.
- Action is taken within the limits of existing laws in different countries and in the spirit of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
- General Assembly: Interpol’s supreme governing body, it meets annually
Three core functions:
- Secure global police communication services
- Operational data services and databases for police
- Operational police support services
Types of Notices
- Blue corner notice— it is issued to collect additional information form it's member countries about a person's identity, location or activities in relation to crime.
Previous Post