Questions
- What are the issues associated with functioning of the Central Information Commission? Suggest solutions to address these issues. (10 marks)
- Elaborate how blockchain technology can be used in governance. Enumerate the advantages and limitations of blockchain technology in governance. (15 marks)
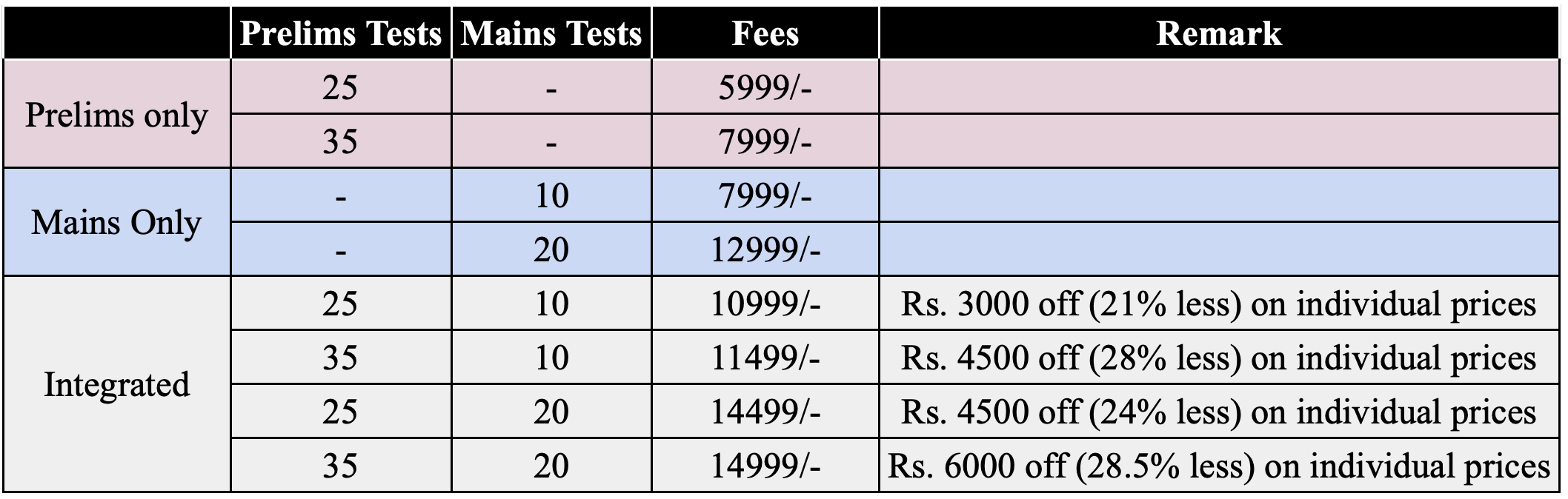
Integrated Prelims + Mains Test Series
For UPSC Prelims and Mains 2023
Model Solutions
1. What are the issues associated with functioning of the Central Information Commission? Suggest solutions to address these issues. (10 marks)
Model Structure
Introduction
- Central Information Commission (CIC) was established by the Central Government in 2005, under the provisions of the Right to Information Act (2005).
- It is a non-constitutional body.
Main Body
- Issues Associated with functioning of CIC-
- Delays and Backlogs:
- On average, the CIC takes 388 days (more than one year) to dispose of an appeal/complaint from the date it was filed before the commission.
- 2.2 lakh+ RTI cases pending at the Central and State Information Commissions (ICs).
- No Penalties:
- Government officials hardly face any punishment for violating the law. (Status report on Functioning of CICs)
- Penalties were imposed in only 2.2% of cases that were disposed of, despite previous analysis showing a rate of about 59% violations which should have triggered the process of penalty imposition
- Vacancy:
- Despite repeated directions from the court, there are still three vacancies in the CIC.
- Lack of Transparency:
- The criteria of selection, etc has not been placed on record.
- Dilution of status and power of CICs
- By vesting powers to determine salaries and service conditions to the Central government
- Delays and Backlogs:
Way Forward
- Underlying issues related to RTI Act should be resolved, so that it can serve the information needs of society.
- By its 2019 order, the apex court had passed a slew of directions to the Central and State governments to fill vacancies across Central and State Information Commissions in a transparent and timely manner.
- Urgent digitization of records and proper record management is important
- Section 4 of RTI (Proactive disclosure of information) should be used as a norm.
- The idea to give constitutional status to CICs needs to discussed
Conclusion
- The right to question is the hallmark of a democracy. Any attack on the RTI law, which has empowered citizens to question those in power, is an attack on the foundation of our democratic republic.
2. Elaborate how blockchain technology can be used in governance. Enumerate the advantages and limitations of blockchain technology in governance. (15 marks)
Model Structure
Introduction
- Blockchain technology is a technology that leads to a chain of blocks, containing digital information stored in a public database. It is a distributed database existing on multiple computers at the same time, which constantly grows as new sets of recordings or blocks are added to it
Main Body
- Possible use cases in Governance
- Governance: Blockchain technology can help in ensuring good governance. It ensures transparency of the public records through the usage of a digital form platform and allows auditing of government documents. Moreover it allows to maintain the authenticity of the document and clearly reduces the processing time.
- Banking: Blockchain can help in avoiding risk of payment losses involved in banking transactions by adopting secure distributed ledger platform. It reduces transaction fees across cross-borders, corporate payments and remittances.
- Food & Supply Chain: It creates a tamper proof record to check the real information about expiration date, product journey from the farm to the shop. The real information of the product can help in improving the reliability and efficiency of the supply chain system.
- Insurance: Blockchain technology can change the ways the insurance documents, claim settlements and fraud handling are carried out. It allows the creation of a transparent, secure, decentralized and immutable insurance network.
- Healthcare: It helps to prioritize patient health at all costs without compromising the quality of the health care service. By establishing a secure chain of networks, blockchain can help in handling the patient records, consent forms, billings and public health monitoring.
- Automotive: Blockchain can solve the challenges in automotive manufacturing, car deliveries, billings. It can help in the creation of an after sales support ecosystem to keep track of the maintenance record of vehicle owners.
- Tourism: Blockchain can reduce the delay time of passenger document handling, creates a decentralized hotel booking ecosystem at the least transaction fee and also keeps passengers private information safe.
- Advantages
- Integrity of the whole process - any block or even a transaction that adds to the chain cannot be edited
- Traceability: With the blockchain ledger, each time an exchange of goods is recorded on a Blockchain, an audit trail is present to trace where the goods came from. This improves security and prevents fraud in exchange-related businesses.
- Security: Blockchain is considered to be a highly secure system due to its digital signature and encryption
- Faster processing: Before the invention of the blockchain, the traditional banking organisation took a lot of time in processing and initiating the transaction but after the blockchain technology speed of the transaction increased to a very high extent.
- Fraud prevention: A system that is based on data stored in a number of places is immune to hackers. It's not that easy to get access to it, and if so, any piece of information can be easily recovered
- Transparency - due to distributed ledger
- Limitations
- Huge power required to verify transactions.
- Technological Challenges – The technological infrastructure of the country and the lack of technical awareness is one of the biggest challenges
- Storage – Data stored in the Blockchain cannot be modified. This demands very heavy resources in terms of storage and may become an issue as the chain of blocks grow
- Skillset and Awareness Issues – Manpower who knows both Domain & Technology is required for blockchain technology management, which may be challenging to find
- Security, Privacy and Regulation – Blockchain data is stored on every node on the network and hence privacy is not an inherent feature
- Legal Challenges – Thee Reserve Bank of India has put forth restriction with respect to virtual currencies based on Blockchain technology and there is a circular to halt the usage of crypto-currency transactions in India
Mains GS Daily Answer Writing - UPSCprep.com
Questions posted at 8AM daily.

