Questions
Model Solutions
Want to get these answers evaluated?
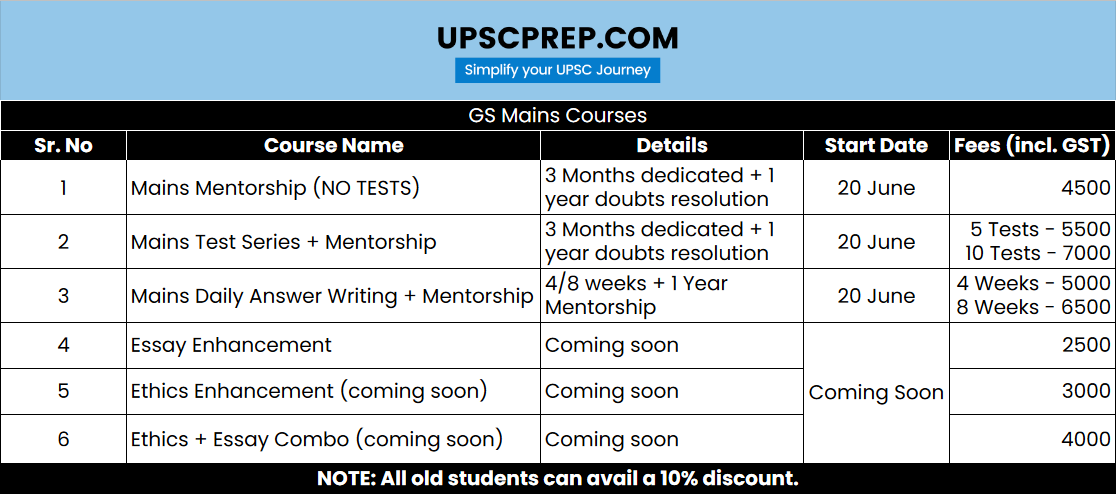
1. Indian Diaspora in the Gulf countries is an asset beset with multiple challenges. Comment. (10 marks)
2. “The present structure of the UN Security Council represents outdated cold-war realities and is in dire need of reform.” Discuss. (15 marks)
Model Structure 1.
Introduction
● According to the World Bank, India is the largest recipient of remittances from diaspora. Bulk of this diaspora is in the Gulf countries. OR
● The Gulf is one of the strategically important regions where more than 8 million Indian diaspora communities live.
Main Body
● Indian Diaspora- Assets
○ Remittances - improves India’s BoP, acts as a source of income for millions of families of NRIs.
○ Social Capital
○ Indian diaspora acts as a part of India’s soft power
○ Indian Diaspora in Political Position
○ Influencing Foreign Policy Decision
● Multiple Challenges
○ Discrimination against Indians in gulf countries
- Poor living conditions of workers
- Laws that bind Indian laborers to unjust working places. Eg Khaleej System ○ Reverse migration
- Unskilled nature of work
- COVID-19
○ Conflict in the gulf region. Eg. Yemen Crisis
Conclusion
● Today, the Indian diaspora is more prosperous than before and its involvement in India’s development is increasing. In this context, India should craft fully conduct diaspora diplomacy so as to turn diaspora potential into diaspora dividend.
Model Structure 2.
Introduction
● The United Nations (UN) was set up, 75 years ago, with the principal aim of maintaining world peace and security.
Main Body
● Need of UNSC reforms
○ Changing geopolitical situation: The Security Council’s membership and working methods reflect a bygone era. Though geopolitics have changed drastically, the UNSC has changed relatively little since 1945, when wartime victors crafted a Charter in their interest and awarded “permanent” veto-wielding Council seats for the Allied victors.
○ Reforms Long Overdue: The UNSC was expanded only once in 1963 to add 4 non-permanent members to the Council. Although the overall membership of the UN has increased from 113 to 193, there has been no change in the composition of the UNSC.
○ Inequitable economic and geographical representation: While Europe is over-represented, Asia is underrepresented. Africa and South America have no representation at all.
○ Crisis of legitimacy and credibility: Stalled reform agenda and various issues including its interventions in Libya and Syria in the name of responsibility have put questions on the credibility of the institution.
○ North-South Divide: The permanent UNSC membership portrays the big North-South divide in the decision making of security measures. For instance, there is no permanent member from Africa, despite the fact that 75% of its work is focused on that continent.
○ Emerging issues: Issues such as deepening economic interdependence, worsening environmental degradation, transnational threats also call for effective multilateral negotiations among the countries based on consensus. Yet, all critical decisions of the UNSC are still being taken by the permanent members of the Security Council.
○ The UN has been unable to respond effectively to the once-in-a-century global crisis triggered by the coronavirus.
● Suggested Reforms
○ Expansion of UNSC permanent membership to make it more inclusive ○ Replacing veto power with consensus based decision making
○ There is a pressing need to enforce greater accountability, coherence and transparency in the Council's activities by making it accountable to UNGA.
Conclusion
● Therefore the demand for reforms in the council has become a necessity to restore its credibility and effectiveness in maintaining international peace and security
Previous Post
