Questions
- Marx has conceptualised the society in terms of different stages. Discuss. 20
- Family may be functional but it does not hold absolute functionality. Discuss. 10
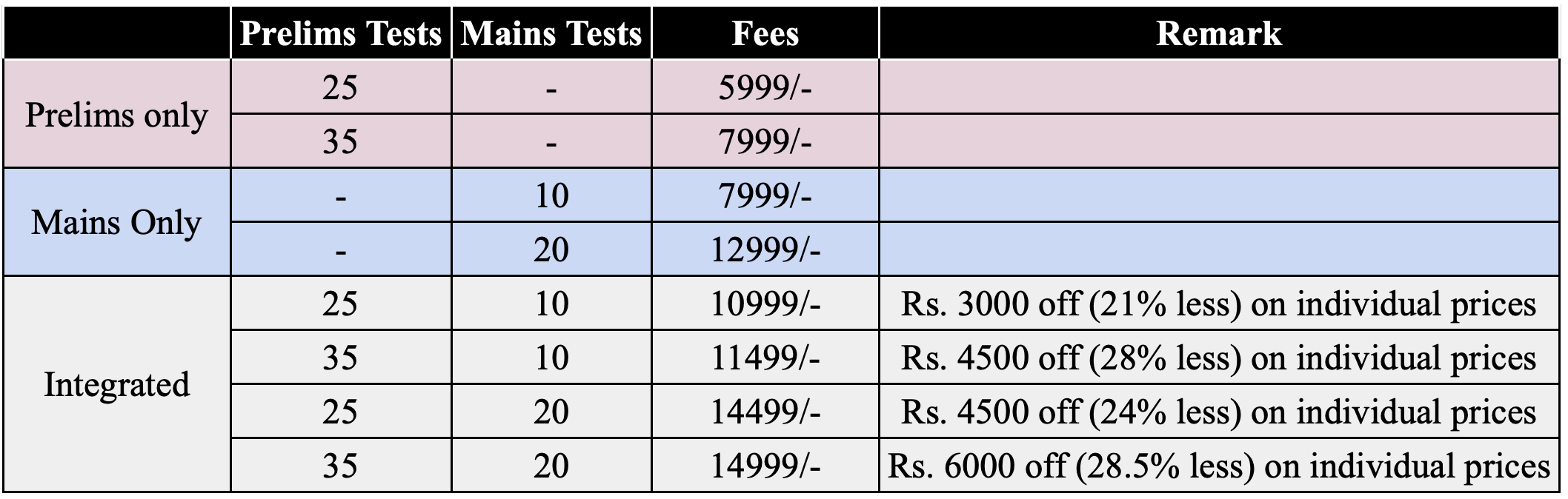
Integrated Prelims + Mains Test Series
For UPSC Prelims and Mains 2023
Model Solutions
Q1. Marx has conceptualised the society in terms of different stages. Discuss. 20
Model Structure
Introduction
- Marx used the term mode of production to refer to the specific organisation of economic production in a given society. It includes the means of production used by a given society, such as factories and other facilities, machines, and raw materials.
Main Body
- Marx gave six evolutionary modes of production. Every new mode of production displaces the earlier one because of various factors like weakness of the earlier systems, antagonism, class struggle etc.
- Modes of production:
- Primitive Communism
- Everyone had equal access to forces of production and was a hunter and gatherer society.
- Relations of production based upon cooperation.
- With the invention of new tools, forces became sophisticated.
- The communal structure of society broke up as a new form of social organisation emerged with the emergence of private ownership.
- Ancient Slave Mode of Production
- Few people have control over skills and tools. Others are subordinates to them.
- Those who held command over tools emerged as masters and those who became dependent became slaves.
- Slaves did not have control on their labours as well.
- Exploitation increased with the increase in population, due to increase in the demand.
- Feudalistic Mode of Production
- Society was divided into landowning feudal lords and landless serfs.
- Land was central to economic activity.
- Serfs were forced to cultivate on the land of feudal lords and had to pay tax and service.
- Capitalist Mode of Production
- Capital is central to production.
- Society is divided into haves and have nots.
- Only labour produces wealth, still wages are too low.
- Workers start feeling alienated.
- Marx argued that exploited workers will unite and class consciousness will rise, which will result in revolt heralding a new mode of production – socialistic mode of production, eventually leading to communism.
- Primitive Communism
Beside these he gave two more futuristic modes of production:
- Socialistic Mode of Production
- It is a transitory mode of production.
- The Proletariat will control the forces of production.
- Marx calls it the dictatorship of the proletariat.
- However Marx argued that control by workers shall also come to an end to realise the true potential of human beings.
- Advanced Communism
- It is the final mode where forces of production will be communally owned as workers too will renounce their rule.
- Everyone will carry on his or her own creative pursuit.
- It will be a classless society.
- It will be the last mode of production as the contradictions and class struggles will be resolved in this mode.
- Marx termed the futuristic modes of production as negation of negation as these modes negate a mode of production which has itself negated another mode of production.
- He was criticised for
- The reductionist approach.
- He predicts that the dialectic process will cease without giving adequate reasoning.
- Asiatic mode of production.
Conclusion
- Thus Marx’s dynamic model of society was based on the continuous change in the forces and relations of production in response to changing material conditions.
Q2. Family may be functional but it does not hold absolute functionality. Discuss. 10
Model Structure
Introduction
- Family is defined by Giddens as ‘a group of persons directly linked by kin connections, the adult members of which assume responsibility of caring for the children'.
Main Body
- Functionalists like Murdock gave four key features of family viz. Reproduction, sexual, economic and education.
- According to Parsons family plays a role of stabilising adult personality through emotional affectional bond. He argued that family does the socialisation of children by inculcating norms and values of the society.
But, - David Cooper argued that family kills the creative potential of children as they are socialised to submit themselves to society
- Engels argues that when the society shifts to communism the family would lose its relevance.
- Vogel and Bell argued that children often become scapegoats in families. As there are constant conflicts between parents.
- Feminists argue that families alot roles to the individual. Male plays the instrumental role and females are allotted the expressive roles.
- Today many alternatives have appeared to the functions of the family like live ins have replaced the sexual function played by family.
Conclusion
- The family may have undergone certain alterations but have not collapsed completely.
