Questions
- What is dryland agriculture? Highlighting its significance, enumerate the issues in dryland agriculture in the case of India. (15 marks)
- Interlinking of rivers is a solution to persisting water scarcity. In this context, explain the issues with Ken Betwa link project and measures to be taken to address them. (10 marks)
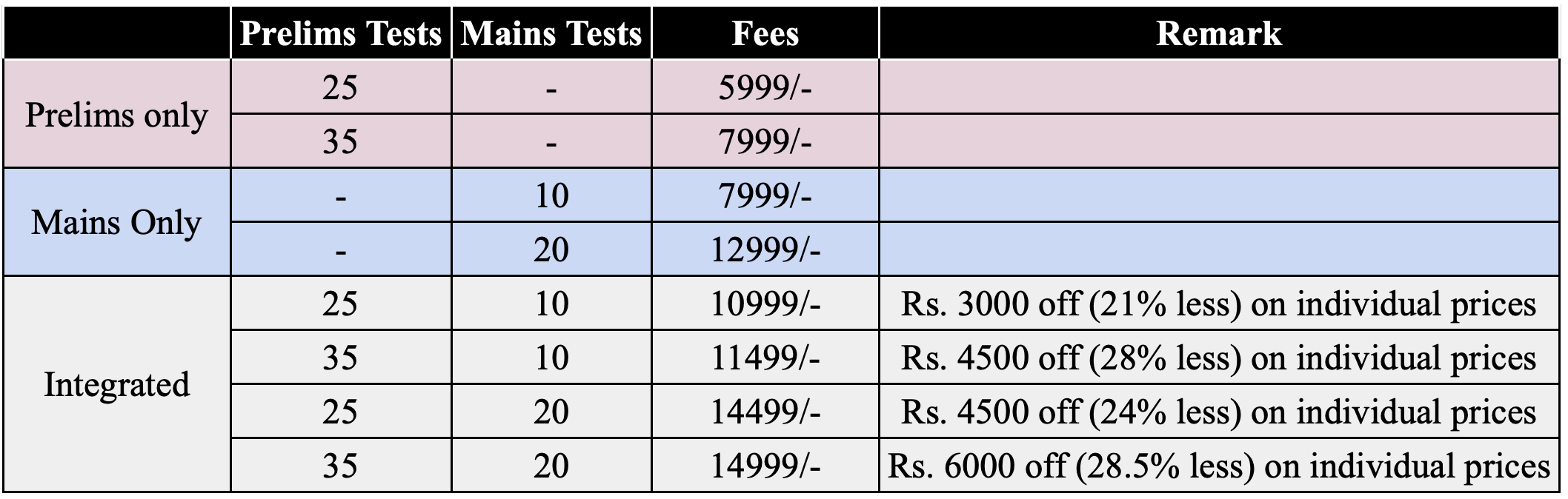
Integrated Prelims + Mains Test Series
For UPSC Prelims and Mains 2023
Model Solutions
Q1. What is dryland agriculture? Highlighting its significance, enumerate the issues in dryland agriculture in the case of India. 15 marks
Model Structure
Introduction
- Dryland farming is a subset of agriculture characterised by less than 75cm annual rainfall and high variability, high dependency on monsoon due to less irrigation sources and majorly subsistence farming.
Main body
- Dryland farming is based on management of three specific features viz crop, land and water. Drought resistant crops, soak pits and embankments for rain water harvesting and minimum tillage for less loss of soil moisture. Based on this, significance of dryland farming includes-
- Approximately 60% agricultural land is rainfed and 25% of it is dryland thus making a lot of farmers dependent on it.
- Though there is less market for nutri cereals when compared to rice and wheat, they are superior when it comes to nutritional security.
- More diversification of food basket and protecting farmers from risk of climate vagaries.
- Less soil exhausting crops thus maintain soil fertility with less use of fertilizers.
- Better shelf life and less processing required as compared to rice mills thus less investments.
- Even with so many benefits, there are some issues involved like-
- Less water availability and nutrient deficient soil due to monoculture in these areas.
- Most of the farmers are small and marginal thus impacting economies of scale and less mechanisation.
- Less profits mean they find it difficult to get institutional credit and have to depend on moneylenders.
- Poor forward and backward linkages thus marketing of products is an issue.
- There are a lot of drought and pest resistant varieties of rice and wheat but not so in case of nutri cereals. This is due to lack of research in this field which affects crop improvement.
Conclusion
- In order to develop this area holistically, keeping in mind the interests of farmers and overall food and nutrition security, there is an urgent need to implement schemes like PM Fasal Bima Yojana, KUSUM, Integrated Watershed Development Program. The International year of millets 2023 is a step in the right direction.
Q2. Interlinking of rivers is a solution to persisting water scarcity. In this context, explain the issues with Ken Betwa link project and measures to be taken to address them. 10 marks
Model Structure
Introduction
- The interlinking of rivers program aims at fulfilling needs of water deficient areas by linking them with areas having rivers with surplus water. The idea was first conceived by Arthur Cotton when he suggested linking the river Ganga with Kaveri for navigation purposes.
Main Body
- Ken Betwa interlink project aims to transfer surplus water from Ken in Madhya Pradesh to Betwa in Uttar Pradesh for drought prone Bundelkhand region. But there are some issues like
- Inter state sharing is an issue and in the case of Ken-Betwa link, Madhya Pradesh has reluctantly given approval. In case of different governments in the centre and states, the issues can complicate.
- Project is implemented without any wildlife and forest clearance. Many committees, especially the Central Empowered Committee of the Supreme Court have questioned it.
- Local tribes and communities have started to protest against it.
- Lack of scientific and social impact assessment.
- These projects can defeat the purpose because of climate change which impacts everyone equally. So the donor state might create problems if it is struck badly by climate change.
- To ensure these issues don’t create a hurdle, some measures can be taken like-
- Proper environmental impact assessment and social impact assessment to ensure all stakeholders are taken into confidence.
- Steps to ensure the root cause of the problem is addressed. Like in target areas, water conservation techniques like rainwater harvesting, groundwater recharge and control of water pollution must be followed.
- Hydrological assessment of surplus river basin, which is not done in case of Ken river.
- Building dams on surplus rivers and allowing flow only during monsoons so that the source river is not affected in the dry season. Also, it will help prevent chances of flooding in surplus rivers.
- Bring consensus among states to ensure strict implementation of such projects irrespective of which government is in power.
Conclusion
- Considering the pros and cons, it can be said that rainwater harvesting and growing of nutri cereals is the ideal step rather than interlinking of rivers which can be catastrophic in the long run.
