Questions
- There is a debate surrounding national language which has potential to affect pluralism and societal peace. Discuss. 10 marks
- India has reserves of rare earth metals more than countries like Australia and USA, but it lags behind when it comes to production. Enumerating the applications of these metals, explain why we are unable to realize the potential. 15 marks
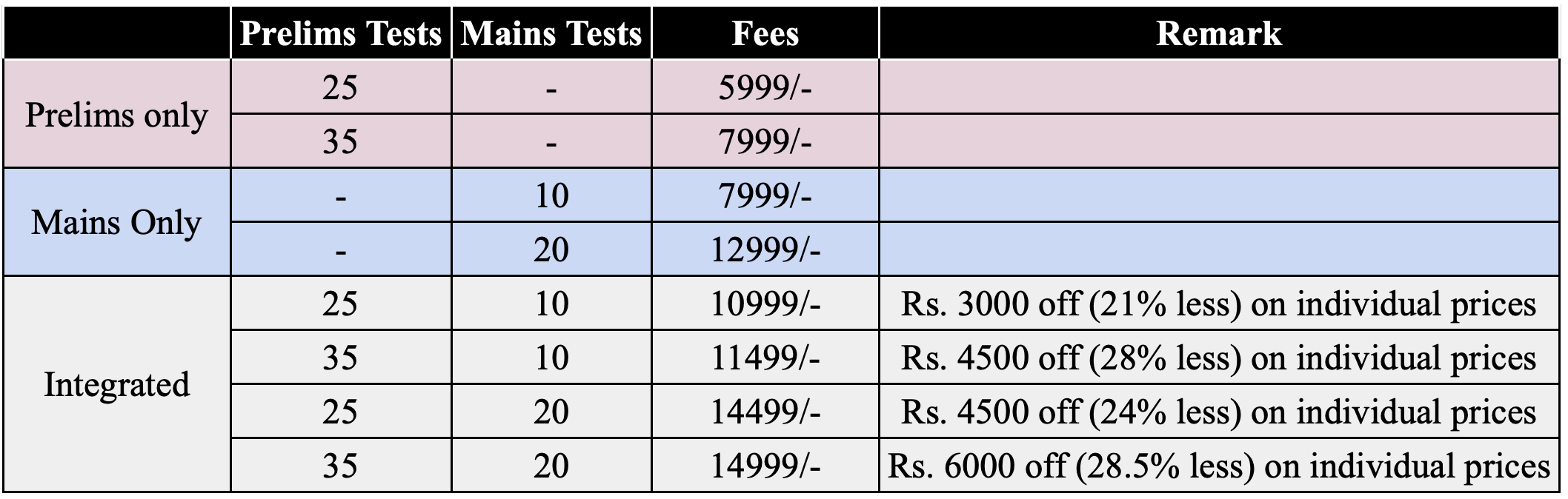
Integrated Prelims + Mains Test Series
For UPSC Prelims and Mains 2023
Model Solutions
Q1. There is a debate surrounding national language which has potential to affect pluralism and societal peace. Discuss. 10 marks
Model Structure
Introduction
- Hindi as a national language is a continuing debate and it came to the forefront when the draft national education policy 2019 gave more importance to Hindi. Southern states contend that Hindi can be a link-language and must not be imposed.
Main body
- Imposition of Hindi has potential to impact diversity and survival of languages with fewer speakers. Hence arguments against imposition of Hindi include
- Native Hindi speakers are roughly estimated to be only 44% thus its imposition can affect learning abilities and education of non-native speakers.
- National integration doesn’t mean homogenization. It can give spark to secessionist tendencies.
- Language is the biggest glue and is the core with which an individual communicates his thoughts and understands human behaviour.
- It is an important factor in preserving social and political identity and linguistic homogenization may lead to political exclusion.
- Apart from these reasons, it can impact employment, education & recreational opportunities, thus affecting nation building and turning demographic dividend into disaster.
- Imposition threatens diversity & federalism and linguistic nationalism can have grave consequences as seen in Europe during world wars.
Conclusion
- There is a need to understand the difference between link language and national language. One brings people closer and the other creates a feeling of superiority.
Q2. India has reserves of rare earth metals more than countries like Australia and USA, but it lags behind when it comes to production. Enumerating the applications of these metals, explain why we are unable to realize the potential. 15 marks
Model Structure
Introduction
- Rare earth metals (REMs) are abundant in Earth’s crust but they hardly occur in a concentrated area, thus making them expensive and uneconomical to explore. China is the largest producer accounting for more than 60% of the global production.
Main Body
- With advancement in technology and increasing use of electronic devices, REMs find plenty of applications like-
- They are lightweight, strong and super conductor thus used in electronic devices.
- For security purposes, they find usage in currency to prevent counterfeiting.
- In advanced medicine, they find applications in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and cancer drugs.
- They are used in the automobile industry for catalytic converters, high-strength magnets and alloys.
- With increasing use of renewable energy, it finds use in wind turbines panels and electric vehicles including batteries.
- With diverse applications, production of REMs must be upscaled but many issues plague the sector like-
- Only the government has a license to explore and mine REMs and for that too only one central and one state PSU is there.
- India has estimated reserves of 6,900 kt but only 9 kts were mined whereas Australia with reserves of 4000 kt produces 22 kt/year.
- India’s current specialization is only upstream i.e extraction, with less capacity to process and purify.
- REMs must have purity of 99.99% but India achieves only 96% purity thus import dependency.
Conclusion
- With demand expected to increase, there is a need to tap in this opportunity as it will fulfill domestic demand and help earn forex. This can be done by deregulating REMs sector and the PSU IREL must diversify focus from just atomic minerals by coming under purview of the Ministry of Mines.
